Introduction
Large-cap value ETFs provide investors with exposure to well-established companies that are considered undervalued based on financial metrics such as price-to-earnings ratios and dividend yields. These funds play a crucial role in portfolio management by offering stability, consistent returns, and lower volatility compared to growth-focused investments. Value investing emphasizes acquiring stocks that trade below their intrinsic value, allowing investors to benefit from long-term appreciation and income generation. Selecting the best large-cap value ETF requires evaluating factors such as expense ratios, sector allocation, historical performance, and dividend payout strategies. Understanding these elements helps investors build a diversified portfolio that aligns with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Understanding Large-Cap Value ETFs
Large-cap value ETFs invest in well-established companies that are considered undervalued based on financial metrics such as price-to-earnings ratios and dividend yields. These funds focus on stocks with strong fundamentals, stable earnings, and lower volatility compared to growth-focused ETFs, which prioritize companies with high revenue expansion potential. While growth ETFs tend to perform well during economic upswings, large-cap value ETFs often provide stability and consistent returns, making them attractive during market downturns. Recent market trends indicate increased investor interest in value ETFs due to rising interest rates and economic uncertainty, as these funds offer defensive characteristics and reliable income generation. Understanding the differences between value and growth ETFs helps investors align their portfolios with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Selection Criteria for Large-Cap Value ETFs
Large-cap value ETFs are evaluated based on several key factors, including expense ratios, portfolio composition, and historical performance. Expense ratios and management fees play a crucial role in determining cost efficiency, with lower fees allowing investors to maximize returns over time. Portfolio composition and sector allocation influence risk exposure, as these ETFs typically focus on stable industries such as financials, healthcare, and consumer staples. Historical performance and risk-adjusted returns provide insights into an ETF’s ability to generate consistent gains while minimizing volatility. Investors seeking long-term stability often prioritize funds with strong track records and diversified holdings to balance growth potential with defensive characteristics.
Key Large-Cap Value ETFs in the Market
VTV, SCHD, and SPYV are among the top-performing large-cap value ETFs, each offering distinct investment strategies. VTV, the Vanguard Value ETF, tracks the CRSP U.S. Large Cap Value Index, providing broad exposure to undervalued large-cap stocks. SCHD, the Schwab U.S. Dividend Equity ETF, focuses on high-dividend-paying companies with strong financial fundamentals, making it attractive for income-seeking investors. SPYV, the SPDR Portfolio S&P 500 Value ETF, follows the S&P 500 Value Index, emphasizing stocks with lower price-to-earnings ratios and stable earnings growth. While VTV offers diversified value exposure, SCHD prioritizes dividend yield, and SPYV provides a balance between value and stability. Investors should consider their financial goals, risk tolerance, and income needs when selecting among these ETFs.
Sector Allocation and Economic Trends
Large-cap value ETFs are influenced by economic cycles, with their performance often tied to broader market conditions. During periods of economic expansion, cyclical sectors such as financials and industrials tend to drive growth, while in downturns, defensive sectors like healthcare and consumer staples provide stability. Leading large-cap value funds typically allocate significant portions to these defensive industries, ensuring resilience against market volatility. Investors favor these ETFs for their ability to maintain steady returns, even during economic uncertainty. The presence of dividend-paying stocks within these funds further enhances their appeal, offering consistent income generation. Understanding sector allocation within large-cap value ETFs helps investors align their portfolios with prevailing economic trends and long-term financial objectives.
Dividend Yields and Income Generation
Large-cap value ETFs play a crucial role in income generation by focusing on companies with strong dividend histories. These funds typically invest in firms that consistently distribute earnings to shareholders, providing a reliable source of passive income. Dividend payout strategies vary across ETFs, with some prioritizing high yields while others emphasize dividend growth. Funds like SCHD and VYM are known for their stable dividend distributions, making them attractive to income-focused investors. Reinvesting dividends allows for compounding gains, as reinvested earnings contribute to additional share accumulation over time. This strategy enhances portfolio growth, ensuring long-term wealth accumulation while maintaining stability in fluctuating markets.
Risk and Volatility Assessment
Large-cap value ETFs generally exhibit lower volatility compared to growth-focused funds, as they invest in established companies with stable earnings and strong fundamentals. Historical trends indicate that these ETFs tend to perform well during economic downturns due to their defensive characteristics, particularly in sectors like healthcare and consumer staples. To mitigate market fluctuations, investors often diversify their portfolios by combining value ETFs with other asset classes, such as bonds or international equities. Additionally, maintaining a long-term perspective helps balance risk, as large-cap value stocks historically recover well from market corrections. Understanding sector allocation and economic cycles allows investors to optimize their portfolios for stability and consistent returns.
Tax Efficiency and Cost Considerations
Large-cap value ETFs are known for their tax efficiency, primarily due to their structure and low turnover rates. Unlike mutual funds, ETFs generally distribute fewer capital gains, reducing tax liabilities for investors. Low expense ratios further enhance returns, as they minimize costs associated with fund management, allowing more capital to compound over time. Investors can optimize tax efficiency by holding ETFs in tax-advantaged accounts or strategically timing sales to minimize taxable distributions. Understanding these factors helps investors maximize after-tax returns while maintaining a diversified portfolio.
Comparing Large-Cap Value ETFs Against Other Investment Options
Large-cap value ETFs provide diversified exposure to undervalued companies, reducing the risk associated with investing in individual stocks. Unlike direct stock investments, these ETFs spread risk across multiple holdings, minimizing the impact of poor performance from any single company. Compared to growth ETFs, which focus on companies with high revenue expansion potential, large-cap value ETFs prioritize stability and consistent returns. Sector-specific funds, on the other hand, concentrate on particular industries, making them more susceptible to economic fluctuations. Large-cap value ETFs fit well into a diversified portfolio by balancing growth opportunities with defensive characteristics, ensuring steady performance across various market conditions.
Investment Strategies for Maximizing Returns
Long-term buy-and-hold strategies for large-cap value ETFs focus on maintaining investments through market fluctuations, allowing compounding returns to build wealth over time. Investors can adjust portfolio allocations based on economic conditions, shifting exposure between defensive and cyclical sectors to optimize performance. ETFs provide passive income through dividend distributions, making them attractive for those seeking steady cash flow. Capital appreciation is achieved as undervalued stocks within these funds grow in value, benefiting from market recoveries and sector rotations. By strategically balancing holdings and reinvesting dividends, investors can enhance returns while minimizing risk.
Conclusion
Large-cap value ETFs offer investors a reliable strategy for long-term wealth accumulation by focusing on undervalued, financially stable companies. These funds provide diversification, passive income through dividends, and resilience against market downturns, making them an attractive choice for conservative and income-focused investors. Comparing options like VTV, SCHD, and SPYV highlights key differences in sector allocation, dividend yields, and risk profiles, helping investors tailor their portfolios to their financial goals. Understanding the tax efficiency, expense ratios, and performance trends of these ETFs allows for informed investment decisions that balance stability and growth potential. Whether seeking steady returns or optimizing portfolio allocations, large-cap value ETFs remain a cornerstone of a well-rounded investment strategy.

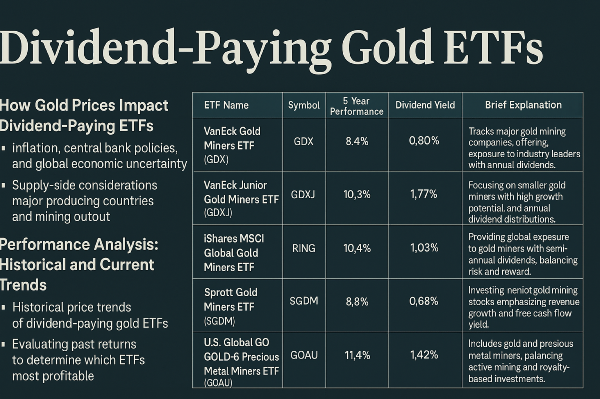
























Introduction
Large-cap value ETFs provide investors with exposure to well-established companies that are considered undervalued based on financial metrics such as price-to-earnings ratios and dividend yields. These funds play a crucial role in portfolio management by offering stability, consistent returns, and lower volatility compared to growth-focused investments. Value investing emphasizes acquiring stocks that trade below their intrinsic value, allowing investors to benefit from long-term appreciation and income generation. Selecting the best large-cap value ETF requires evaluating factors such as expense ratios, sector allocation, historical performance, and dividend payout strategies. Understanding these elements helps investors build a diversified portfolio that aligns with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Understanding Large-Cap Value ETFs
Large-cap value ETFs invest in well-established companies that are considered undervalued based on financial metrics such as price-to-earnings ratios and dividend yields. These funds focus on stocks with strong fundamentals, stable earnings, and lower volatility compared to growth-focused ETFs, which prioritize companies with high revenue expansion potential. While growth ETFs tend to perform well during economic upswings, large-cap value ETFs often provide stability and consistent returns, making them attractive during market downturns. Recent market trends indicate increased investor interest in value ETFs due to rising interest rates and economic uncertainty, as these funds offer defensive characteristics and reliable income generation. Understanding the differences between value and growth ETFs helps investors align their portfolios with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Selection Criteria for Large-Cap Value ETFs
Large-cap value ETFs are evaluated based on several key factors, including expense ratios, portfolio composition, and historical performance. Expense ratios and management fees play a crucial role in determining cost efficiency, with lower fees allowing investors to maximize returns over time. Portfolio composition and sector allocation influence risk exposure, as these ETFs typically focus on stable industries such as financials, healthcare, and consumer staples. Historical performance and risk-adjusted returns provide insights into an ETF’s ability to generate consistent gains while minimizing volatility. Investors seeking long-term stability often prioritize funds with strong track records and diversified holdings to balance growth potential with defensive characteristics.
Key Large-Cap Value ETFs in the Market
VTV, SCHD, and SPYV are among the top-performing large-cap value ETFs, each offering distinct investment strategies. VTV, the Vanguard Value ETF, tracks the CRSP U.S. Large Cap Value Index, providing broad exposure to undervalued large-cap stocks. SCHD, the Schwab U.S. Dividend Equity ETF, focuses on high-dividend-paying companies with strong financial fundamentals, making it attractive for income-seeking investors. SPYV, the SPDR Portfolio S&P 500 Value ETF, follows the S&P 500 Value Index, emphasizing stocks with lower price-to-earnings ratios and stable earnings growth. While VTV offers diversified value exposure, SCHD prioritizes dividend yield, and SPYV provides a balance between value and stability. Investors should consider their financial goals, risk tolerance, and income needs when selecting among these ETFs.
Sector Allocation and Economic Trends
Large-cap value ETFs are influenced by economic cycles, with their performance often tied to broader market conditions. During periods of economic expansion, cyclical sectors such as financials and industrials tend to drive growth, while in downturns, defensive sectors like healthcare and consumer staples provide stability. Leading large-cap value funds typically allocate significant portions to these defensive industries, ensuring resilience against market volatility. Investors favor these ETFs for their ability to maintain steady returns, even during economic uncertainty. The presence of dividend-paying stocks within these funds further enhances their appeal, offering consistent income generation. Understanding sector allocation within large-cap value ETFs helps investors align their portfolios with prevailing economic trends and long-term financial objectives.
Dividend Yields and Income Generation
Large-cap value ETFs play a crucial role in income generation by focusing on companies with strong dividend histories. These funds typically invest in firms that consistently distribute earnings to shareholders, providing a reliable source of passive income. Dividend payout strategies vary across ETFs, with some prioritizing high yields while others emphasize dividend growth. Funds like SCHD and VYM are known for their stable dividend distributions, making them attractive to income-focused investors. Reinvesting dividends allows for compounding gains, as reinvested earnings contribute to additional share accumulation over time. This strategy enhances portfolio growth, ensuring long-term wealth accumulation while maintaining stability in fluctuating markets.
Risk and Volatility Assessment
Large-cap value ETFs generally exhibit lower volatility compared to growth-focused funds, as they invest in established companies with stable earnings and strong fundamentals. Historical trends indicate that these ETFs tend to perform well during economic downturns due to their defensive characteristics, particularly in sectors like healthcare and consumer staples. To mitigate market fluctuations, investors often diversify their portfolios by combining value ETFs with other asset classes, such as bonds or international equities. Additionally, maintaining a long-term perspective helps balance risk, as large-cap value stocks historically recover well from market corrections. Understanding sector allocation and economic cycles allows investors to optimize their portfolios for stability and consistent returns.
Tax Efficiency and Cost Considerations
Large-cap value ETFs are known for their tax efficiency, primarily due to their structure and low turnover rates. Unlike mutual funds, ETFs generally distribute fewer capital gains, reducing tax liabilities for investors. Low expense ratios further enhance returns, as they minimize costs associated with fund management, allowing more capital to compound over time. Investors can optimize tax efficiency by holding ETFs in tax-advantaged accounts or strategically timing sales to minimize taxable distributions. Understanding these factors helps investors maximize after-tax returns while maintaining a diversified portfolio.
Comparing Large-Cap Value ETFs Against Other Investment Options
Large-cap value ETFs provide diversified exposure to undervalued companies, reducing the risk associated with investing in individual stocks. Unlike direct stock investments, these ETFs spread risk across multiple holdings, minimizing the impact of poor performance from any single company. Compared to growth ETFs, which focus on companies with high revenue expansion potential, large-cap value ETFs prioritize stability and consistent returns. Sector-specific funds, on the other hand, concentrate on particular industries, making them more susceptible to economic fluctuations. Large-cap value ETFs fit well into a diversified portfolio by balancing growth opportunities with defensive characteristics, ensuring steady performance across various market conditions.
Investment Strategies for Maximizing Returns
Long-term buy-and-hold strategies for large-cap value ETFs focus on maintaining investments through market fluctuations, allowing compounding returns to build wealth over time. Investors can adjust portfolio allocations based on economic conditions, shifting exposure between defensive and cyclical sectors to optimize performance. ETFs provide passive income through dividend distributions, making them attractive for those seeking steady cash flow. Capital appreciation is achieved as undervalued stocks within these funds grow in value, benefiting from market recoveries and sector rotations. By strategically balancing holdings and reinvesting dividends, investors can enhance returns while minimizing risk.
Conclusion
Large-cap value ETFs offer investors a reliable strategy for long-term wealth accumulation by focusing on undervalued, financially stable companies. These funds provide diversification, passive income through dividends, and resilience against market downturns, making them an attractive choice for conservative and income-focused investors. Comparing options like VTV, SCHD, and SPYV highlights key differences in sector allocation, dividend yields, and risk profiles, helping investors tailor their portfolios to their financial goals. Understanding the tax efficiency, expense ratios, and performance trends of these ETFs allows for informed investment decisions that balance stability and growth potential. Whether seeking steady returns or optimizing portfolio allocations, large-cap value ETFs remain a cornerstone of a well-rounded investment strategy.