Introduction
Mega-cap stocks represent the largest publicly traded companies, typically with market capitalizations exceeding $200 billion. These companies dominate their industries, wielding significant influence over global markets and economic trends. Their size and stability make them attractive to investors seeking lower volatility and consistent returns. As these companies shape financial markets, their performance often serves as an indicator of broader economic conditions, guiding investment decisions across various sectors.
What Qualifies as a Mega-Cap Stock?
Mega-cap stocks are the largest publicly traded companies, typically with market capitalizations exceeding $200 billion. This classification distinguishes them from large-cap stocks, which generally have market values above $10 billion, and giant-cap stocks, which surpass $100 billion. While the exact threshold for mega-cap status can fluctuate based on market conditions, these companies consistently rank among the most valuable firms globally. Their size and financial strength allow them to exert significant influence over stock indices, economic trends, and investor sentiment.
Compared to large-cap and giant-cap stocks, mega-cap companies exhibit greater stability and lower volatility. The extensive resources of Mega Stocks enable them to invest in innovation, acquisitions, and expansion, further solidifying their market positions. These companies frequently appear in major indices such as the S&P 500 and Nasdaq-100, reinforcing their importance in the financial landscape. Key characteristics of mega-cap stocks include strong brand recognition, diversified revenue streams, and consistent profitability. Many of these companies operate across multiple industries, reducing their exposure to sector-specific risks.
How Many Mega-Cap Stocks Exist Today?
The number of mega-cap stocks fluctuates based on market conditions, economic trends, and corporate growth. As of 2024, there are over 50 publicly traded companies classified as mega-cap stocks, each with a market capitalization exceeding $200 billion. These companies represent the largest and most influential firms in global markets, spanning various industries such as technology, finance, healthcare, and consumer goods.
The total count of mega-cap stocks can change as companies experience valuation shifts due to earnings performance, mergers, or broader market movements. The U.S. market hosts a significant portion of these companies, including technology giants like Microsoft, Apple, and Nvidia.
Industry Breakdown of Mega-Cap Stocks
Mega-cap stocks are primarily concentrated in a few dominant industries, reflecting their market influence and financial strength. Technology remains the leading sector, with companies like Apple, Microsoft, and Nvidia driving innovation and global economic trends. Finance also plays a significant role, with institutions such as JPMorgan Chase and Berkshire Hathaway maintaining strong market positions. Consumer sectors, including retail and healthcare, contribute to the mega-cap category, with firms like Amazon and Johnson & Johnson demonstrating consistent revenue growth and industry leadership.
These sectors collectively shape the stock market, influencing investment strategies and economic policies. Consumer-focused mega-cap stocks leverage their extensive customer bases and diversified product offerings to maintain steady revenue streams, making them attractive for long-term investors.
Historical Growth and Market Trends
Mega-cap stocks have evolved significantly over time, reflecting shifts in market dynamics and economic conditions. In the late 20th century, industrial and financial firms dominated the mega-cap category, with companies like General Electric and ExxonMobil leading the market. However, the rise of technology in the 21st century has reshaped the landscape, with firms such as Apple, Microsoft, and Amazon emerging as dominant players. Several companies have transitioned into or out of the mega-cap classification due to changes in valuation, industry trends, and economic cycles.
Key economic events have played a crucial role in influencing the growth of mega-cap stocks. The dot-com boom of the late 1990s propelled technology firms into prominence, while the 2008 financial crisis reshaped the composition of leading companies. More recently, the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated digital adoption, benefiting tech giants and reinforcing their market dominance.
Investment Implications of Mega-Cap Stocks
Mega-cap stocks play a crucial role in portfolio allocation strategies, offering stability and long-term growth potential. Investors often allocate a portion of their portfolios to these companies due to their strong financial performance and industry dominance. A well-balanced portfolio may include a mix of mega-cap stocks alongside mid-cap and small-cap investments to optimize diversification.
The inclusion of mega-cap stocks in major indices further reinforces their reliability as long-term assets. Risk vs. reward considerations are essential when investing in mega-cap stocks. While these companies provide stability and consistent returns, their size can limit rapid growth compared to smaller firms. Additionally, mega-cap stocks can be affected by regulatory scrutiny and market saturation, which may impact their future expansion.
Case Studies: Notable Mega-Cap Stocks
Mega-cap stocks represent some of the most influential companies in global markets, often setting industry standards and driving economic trends. Notable examples include Apple, Microsoft, Amazon, and Nvidia, each boasting market capitalizations exceeding $200 billion. These companies have established themselves as leaders in technology, e-commerce, and artificial intelligence, leveraging innovation and strategic expansion to maintain their dominance.
Analyzing the growth trajectories and financial performance of mega-cap stocks reveals key patterns in their expansion strategies.
These firms demonstrate how diversification and innovation contribute to sustained financial performance. Investors can learn valuable lessons from the success of mega-cap stocks. One key takeaway is the importance of long-term strategic planning, as these companies prioritize innovation and market expansion over short-term gains.
Challenges Faced by Mega-Cap Companies
Mega-cap companies face increasing regulatory scrutiny due to their market dominance and influence over global economies. Governments and financial regulators closely monitor these firms to ensure fair competition, consumer protection, and compliance with antitrust laws. Stricter regulations can impact business operations, requiring companies to adapt to evolving legal frameworks.
Additionally, mega-cap stocks often encounter challenges related to data privacy, cybersecurity, and financial transparency, further complicating their ability to maintain growth while adhering to regulatory requirements. Market shifts, consumer preferences, and disruptive technologies can threaten their long-term growth potential. The sustainability of mega-cap dominance over time depends on their ability to adapt to changing economic conditions and industry trends. Companies that fail to innovate or diversify their revenue streams risk losing their market leadership. Investors must assess these factors when considering long-term positions in mega-cap companies.
Conclusion
Mega-cap stocks represent the most influential and financially stable companies in global markets, driving industry innovation and shaping economic policies. Their market dominance offers investors security and long-term growth potential, but challenges such as regulatory scrutiny and competition risks must be considered. Understanding their sector distribution, historical performance, and investment strategies helps investors make informed decisions when incorporating these stocks into their portfolios.
While mega-cap companies continue to evolve, their ability to adapt to market trends will determine their sustainability in the financial landscape. Investors who recognize these dynamics can optimize their portfolios to balance stability and growth effectively.


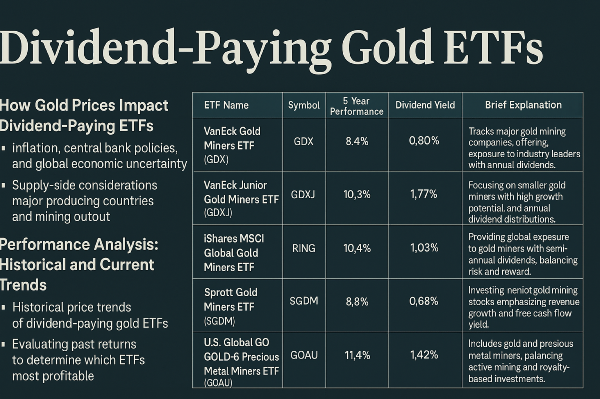
















Introduction
Mega-cap stocks represent the largest publicly traded companies, typically with market capitalizations exceeding $200 billion. These companies dominate their industries, wielding significant influence over global markets and economic trends. Their size and stability make them attractive to investors seeking lower volatility and consistent returns. As these companies shape financial markets, their performance often serves as an indicator of broader economic conditions, guiding investment decisions across various sectors.
What Qualifies as a Mega-Cap Stock?
Mega-cap stocks are the largest publicly traded companies, typically with market capitalizations exceeding $200 billion. This classification distinguishes them from large-cap stocks, which generally have market values above $10 billion, and giant-cap stocks, which surpass $100 billion. While the exact threshold for mega-cap status can fluctuate based on market conditions, these companies consistently rank among the most valuable firms globally. Their size and financial strength allow them to exert significant influence over stock indices, economic trends, and investor sentiment.
Compared to large-cap and giant-cap stocks, mega-cap companies exhibit greater stability and lower volatility. The extensive resources of Mega Stocks enable them to invest in innovation, acquisitions, and expansion, further solidifying their market positions. These companies frequently appear in major indices such as the S&P 500 and Nasdaq-100, reinforcing their importance in the financial landscape. Key characteristics of mega-cap stocks include strong brand recognition, diversified revenue streams, and consistent profitability. Many of these companies operate across multiple industries, reducing their exposure to sector-specific risks.
How Many Mega-Cap Stocks Exist Today?
The number of mega-cap stocks fluctuates based on market conditions, economic trends, and corporate growth. As of 2024, there are over 50 publicly traded companies classified as mega-cap stocks, each with a market capitalization exceeding $200 billion. These companies represent the largest and most influential firms in global markets, spanning various industries such as technology, finance, healthcare, and consumer goods.
The total count of mega-cap stocks can change as companies experience valuation shifts due to earnings performance, mergers, or broader market movements. The U.S. market hosts a significant portion of these companies, including technology giants like Microsoft, Apple, and Nvidia.
Industry Breakdown of Mega-Cap Stocks
Mega-cap stocks are primarily concentrated in a few dominant industries, reflecting their market influence and financial strength. Technology remains the leading sector, with companies like Apple, Microsoft, and Nvidia driving innovation and global economic trends. Finance also plays a significant role, with institutions such as JPMorgan Chase and Berkshire Hathaway maintaining strong market positions. Consumer sectors, including retail and healthcare, contribute to the mega-cap category, with firms like Amazon and Johnson & Johnson demonstrating consistent revenue growth and industry leadership.
These sectors collectively shape the stock market, influencing investment strategies and economic policies. Consumer-focused mega-cap stocks leverage their extensive customer bases and diversified product offerings to maintain steady revenue streams, making them attractive for long-term investors.
Historical Growth and Market Trends
Mega-cap stocks have evolved significantly over time, reflecting shifts in market dynamics and economic conditions. In the late 20th century, industrial and financial firms dominated the mega-cap category, with companies like General Electric and ExxonMobil leading the market. However, the rise of technology in the 21st century has reshaped the landscape, with firms such as Apple, Microsoft, and Amazon emerging as dominant players. Several companies have transitioned into or out of the mega-cap classification due to changes in valuation, industry trends, and economic cycles.
Key economic events have played a crucial role in influencing the growth of mega-cap stocks. The dot-com boom of the late 1990s propelled technology firms into prominence, while the 2008 financial crisis reshaped the composition of leading companies. More recently, the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated digital adoption, benefiting tech giants and reinforcing their market dominance.
Investment Implications of Mega-Cap Stocks
Mega-cap stocks play a crucial role in portfolio allocation strategies, offering stability and long-term growth potential. Investors often allocate a portion of their portfolios to these companies due to their strong financial performance and industry dominance. A well-balanced portfolio may include a mix of mega-cap stocks alongside mid-cap and small-cap investments to optimize diversification.
The inclusion of mega-cap stocks in major indices further reinforces their reliability as long-term assets. Risk vs. reward considerations are essential when investing in mega-cap stocks. While these companies provide stability and consistent returns, their size can limit rapid growth compared to smaller firms. Additionally, mega-cap stocks can be affected by regulatory scrutiny and market saturation, which may impact their future expansion.
Case Studies: Notable Mega-Cap Stocks
Mega-cap stocks represent some of the most influential companies in global markets, often setting industry standards and driving economic trends. Notable examples include Apple, Microsoft, Amazon, and Nvidia, each boasting market capitalizations exceeding $200 billion. These companies have established themselves as leaders in technology, e-commerce, and artificial intelligence, leveraging innovation and strategic expansion to maintain their dominance.
Analyzing the growth trajectories and financial performance of mega-cap stocks reveals key patterns in their expansion strategies. These firms demonstrate how diversification and innovation contribute to sustained financial performance. Investors can learn valuable lessons from the success of mega-cap stocks. One key takeaway is the importance of long-term strategic planning, as these companies prioritize innovation and market expansion over short-term gains.
Challenges Faced by Mega-Cap Companies
Mega-cap companies face increasing regulatory scrutiny due to their market dominance and influence over global economies. Governments and financial regulators closely monitor these firms to ensure fair competition, consumer protection, and compliance with antitrust laws. Stricter regulations can impact business operations, requiring companies to adapt to evolving legal frameworks.
Additionally, mega-cap stocks often encounter challenges related to data privacy, cybersecurity, and financial transparency, further complicating their ability to maintain growth while adhering to regulatory requirements. Market shifts, consumer preferences, and disruptive technologies can threaten their long-term growth potential. The sustainability of mega-cap dominance over time depends on their ability to adapt to changing economic conditions and industry trends. Companies that fail to innovate or diversify their revenue streams risk losing their market leadership. Investors must assess these factors when considering long-term positions in mega-cap companies.
Conclusion Mega-cap stocks represent the most influential and financially stable companies in global markets, driving industry innovation and shaping economic policies. Their market dominance offers investors security and long-term growth potential, but challenges such as regulatory scrutiny and competition risks must be considered. Understanding their sector distribution, historical performance, and investment strategies helps investors make informed decisions when incorporating these stocks into their portfolios.
While mega-cap companies continue to evolve, their ability to adapt to market trends will determine their sustainability in the financial landscape. Investors who recognize these dynamics can optimize their portfolios to balance stability and growth effectively.