Introduction
Large-cap growth investing focuses on companies with strong earnings potential and market leadership, making it a preferred strategy for investors seeking long-term capital appreciation. Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) provide an efficient way to gain diversified exposure to these stocks, reducing individual security risk while maintaining access to high-growth opportunities. By understanding the various criteria, investors can optimize their portfolios to balance risk and reward while capitalizing on the growth potential of leading companies.
Characteristics of Large-Cap Growth ETFs
Large-cap growth stocks are companies with a market capitalization exceeding $10 billion that exhibit strong revenue and earnings growth potential. These stocks typically belong to industries such as technology, healthcare, and consumer discretionary, where innovation and market expansion drive performance. Large-cap growth ETFs pool these stocks into a single investment vehicle, allowing investors to gain diversified exposure to high-growth companies while minimizing individual stock risk. Several key factors contribute to the growth of large-cap companies, including strong financial metrics, competitive advantages, and industry leadership.
Companies with high return on equity (ROE) and consistent revenue growth tend to outperform their peers, attracting investor confidence.
Growth-focused ETFs differ from value-focused ETFs in their investment approach and risk profile. While growth ETFs prioritize companies with high earnings potential and reinvestment strategies, value ETFs focus on undervalued stocks with strong fundamentals and stable dividends. Growth stocks tend to be more volatile, while value stocks offer lower volatility and steady income.
Top Large-Cap Growth ETFs in the Market
Large-cap growth ETFs such as VUG, QQQ, and SCHG provide investors with exposure to high-growth companies that dominate their respective industries. VUG, managed by Vanguard, tracks the CRSP U.S. Large Cap Growth Index, offering a diversified portfolio of leading growth stocks. QQQ, issued by Invesco, follows the Nasdaq-100 Index, making it heavily weighted toward technology companies. SCHG, managed by Schwab, tracks the Dow Jones U.S. Large-Cap Growth Total Stock Market Index, providing broad exposure to large-cap growth stocks across multiple sectors. These ETFs are popular among investors seeking long-term capital appreciation through companies with strong earnings potential.
Comparing the holdings and expense ratios of these ETFs reveals key differences. The top holdings in these ETFs include technology giants such as Microsoft, Apple, and Nvidia, which collectively account for a significant portion of their weightings. Historical performance data indicates that QQQ has delivered higher returns during technology-driven bull markets, while VUG and SCHG provide more balanced exposure across various sectors. The influence of mega-cap stocks within these ETFs can lead to higher volatility, particularly when leading companies experience price swings.
Performance Analysis of Large-Cap Growth ETFs
Large-cap growth ETFs have historically delivered strong returns, often outperforming broad market indices during bullish periods. Funds such as SCHG, QQQ, and VUG have demonstrated impressive long-term performance. However, these ETFs tend to exhibit higher volatility due to their concentration in growth-oriented sectors like technology and consumer discretionary. Economic cycles play a crucial role in shaping the performance of large-cap growth ETFs.
During periods of economic expansion, growth stocks benefit from increased consumer spending and corporate investment. During recessions or market corrections, these funds may experience sharp declines as investors shift toward defensive assets. The long-term potential of growth-focused ETFs remains strong, particularly for investors with extended time horizons.
Expense Ratios and Cost Considerations
Low expense ratios play a crucial role in maximizing returns for investors in large-cap growth ETFs. Since ETFs passively track indices, their management costs are typically lower than actively managed funds. Over time, even small differences in expense ratios can significantly impact overall investment performance. Investors seeking to optimize returns should prioritize funds with lower fees. Comparing fees across major large-cap growth ETFs reveals notable differences.
ETFs such as VUG and SCHG offer competitive expense ratios of 0.04%, making them cost-effective options for long-term investors. In contrast, QQQ has a higher expense ratio of 0.20%, reflecting its focus on Nasdaq-listed stocks and active trading volume. Additional costs such as bid-ask spreads and liquidity concerns also impact ETF performance.
Sector Exposure and Diversification Benefits
Large-cap growth ETFs allocate holdings across various sectors, with technology, consumer discretionary, and healthcare stocks often receiving the highest weightings. Technology remains the dominant sector in many growth-focused ETFs. These sector allocations shape the overall performance of large-cap growth ETFs, influencing returns based on industry trends and economic conditions. The dominance of technology, consumer discretionary, and healthcare stocks in large-cap growth ETFs reflects their market influence and growth potential. Sector trends significantly impact ETF returns and investor strategies, as economic cycles influence the performance of different industries.
Risks Associated with Large-Cap Growth ETFs
Large-cap growth ETFs are highly sensitive to market volatility, particularly during economic downturns. Since these funds allocate a significant portion of their holdings to high-growth companies, they tend to experience sharp price fluctuations when investor sentiment shifts. During periods of economic uncertainty, growth stocks often underperform as investors move toward defensive assets such as bonds and dividend-paying stocks.
Concentration risk is another challenge associated with large-cap growth ETFs, as they rely heavily on a few dominant stocks. Investors should consider how concentrated holdings impact overall portfolio stability and risk exposure. Mitigating risk in large-cap growth ETFs requires strategic diversification.
How to Choose the Right Large-Cap Growth ETF
Selecting the right large-cap growth ETF requires careful evaluation of individual financial goals and risk tolerance. Investors seeking long-term capital appreciation should prioritize ETFs with strong growth potential, while those focused on stability may prefer funds with lower volatility. Risk tolerance plays a crucial role, as large-cap growth ETFs tend to experience higher price fluctuations compared to value-oriented funds. Comparing fund objectives, expense ratios, and sector weightings is essential for making an informed decision. Sector weightings also vary. Liquidity and long-term investment outlook are additional factors to consider when choosing a large-cap growth ETF. Investors should analyze these differences to select an ETF that aligns with their investment preferences.
Conclusion
Large-cap growth ETFs provide investors with an efficient way to gain exposure to high-growth companies while maintaining diversification across key sectors. ETFs such as VUG, QQQ, and SCHG offer distinct advantages in terms of expense ratios, sector allocations, and historical performance, allowing investors to select funds that best align with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
While these ETFs benefit from strong returns during economic expansions, they also carry concentration risks due to their reliance on dominant stocks, particularly in the technology sector. Careful consideration of liquidity, expense ratios, and macroeconomic trends helps investors optimize their portfolios for long-term growth. By selecting the right large-cap growth ETF, investors can balance risk and reward while capitalizing on the potential of market-leading companies.

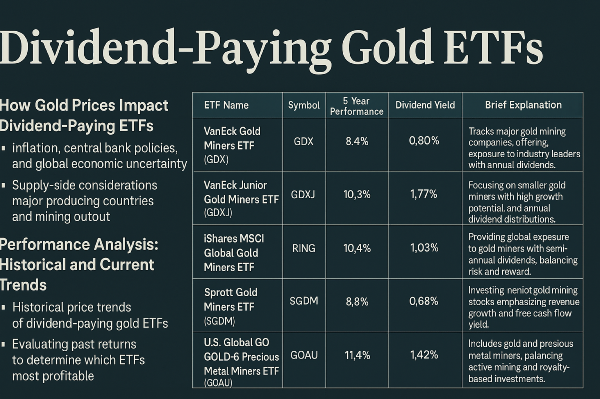
















Introduction
Large-cap growth investing focuses on companies with strong earnings potential and market leadership, making it a preferred strategy for investors seeking long-term capital appreciation. Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) provide an efficient way to gain diversified exposure to these stocks, reducing individual security risk while maintaining access to high-growth opportunities. By understanding the various criteria, investors can optimize their portfolios to balance risk and reward while capitalizing on the growth potential of leading companies.
Characteristics of Large-Cap Growth ETFs
Large-cap growth stocks are companies with a market capitalization exceeding $10 billion that exhibit strong revenue and earnings growth potential. These stocks typically belong to industries such as technology, healthcare, and consumer discretionary, where innovation and market expansion drive performance. Large-cap growth ETFs pool these stocks into a single investment vehicle, allowing investors to gain diversified exposure to high-growth companies while minimizing individual stock risk. Several key factors contribute to the growth of large-cap companies, including strong financial metrics, competitive advantages, and industry leadership.
Companies with high return on equity (ROE) and consistent revenue growth tend to outperform their peers, attracting investor confidence. Growth-focused ETFs differ from value-focused ETFs in their investment approach and risk profile. While growth ETFs prioritize companies with high earnings potential and reinvestment strategies, value ETFs focus on undervalued stocks with strong fundamentals and stable dividends. Growth stocks tend to be more volatile, while value stocks offer lower volatility and steady income.
Top Large-Cap Growth ETFs in the Market
Large-cap growth ETFs such as VUG, QQQ, and SCHG provide investors with exposure to high-growth companies that dominate their respective industries. VUG, managed by Vanguard, tracks the CRSP U.S. Large Cap Growth Index, offering a diversified portfolio of leading growth stocks. QQQ, issued by Invesco, follows the Nasdaq-100 Index, making it heavily weighted toward technology companies. SCHG, managed by Schwab, tracks the Dow Jones U.S. Large-Cap Growth Total Stock Market Index, providing broad exposure to large-cap growth stocks across multiple sectors. These ETFs are popular among investors seeking long-term capital appreciation through companies with strong earnings potential.
Comparing the holdings and expense ratios of these ETFs reveals key differences. The top holdings in these ETFs include technology giants such as Microsoft, Apple, and Nvidia, which collectively account for a significant portion of their weightings. Historical performance data indicates that QQQ has delivered higher returns during technology-driven bull markets, while VUG and SCHG provide more balanced exposure across various sectors. The influence of mega-cap stocks within these ETFs can lead to higher volatility, particularly when leading companies experience price swings.
Performance Analysis of Large-Cap Growth ETFs
Large-cap growth ETFs have historically delivered strong returns, often outperforming broad market indices during bullish periods. Funds such as SCHG, QQQ, and VUG have demonstrated impressive long-term performance. However, these ETFs tend to exhibit higher volatility due to their concentration in growth-oriented sectors like technology and consumer discretionary. Economic cycles play a crucial role in shaping the performance of large-cap growth ETFs.
During periods of economic expansion, growth stocks benefit from increased consumer spending and corporate investment. During recessions or market corrections, these funds may experience sharp declines as investors shift toward defensive assets. The long-term potential of growth-focused ETFs remains strong, particularly for investors with extended time horizons.
Expense Ratios and Cost Considerations
Low expense ratios play a crucial role in maximizing returns for investors in large-cap growth ETFs. Since ETFs passively track indices, their management costs are typically lower than actively managed funds. Over time, even small differences in expense ratios can significantly impact overall investment performance. Investors seeking to optimize returns should prioritize funds with lower fees. Comparing fees across major large-cap growth ETFs reveals notable differences.
ETFs such as VUG and SCHG offer competitive expense ratios of 0.04%, making them cost-effective options for long-term investors. In contrast, QQQ has a higher expense ratio of 0.20%, reflecting its focus on Nasdaq-listed stocks and active trading volume. Additional costs such as bid-ask spreads and liquidity concerns also impact ETF performance.
Sector Exposure and Diversification Benefits
Large-cap growth ETFs allocate holdings across various sectors, with technology, consumer discretionary, and healthcare stocks often receiving the highest weightings. Technology remains the dominant sector in many growth-focused ETFs. These sector allocations shape the overall performance of large-cap growth ETFs, influencing returns based on industry trends and economic conditions. The dominance of technology, consumer discretionary, and healthcare stocks in large-cap growth ETFs reflects their market influence and growth potential. Sector trends significantly impact ETF returns and investor strategies, as economic cycles influence the performance of different industries.
Risks Associated with Large-Cap Growth ETFs
Large-cap growth ETFs are highly sensitive to market volatility, particularly during economic downturns. Since these funds allocate a significant portion of their holdings to high-growth companies, they tend to experience sharp price fluctuations when investor sentiment shifts. During periods of economic uncertainty, growth stocks often underperform as investors move toward defensive assets such as bonds and dividend-paying stocks.
Concentration risk is another challenge associated with large-cap growth ETFs, as they rely heavily on a few dominant stocks. Investors should consider how concentrated holdings impact overall portfolio stability and risk exposure. Mitigating risk in large-cap growth ETFs requires strategic diversification.
How to Choose the Right Large-Cap Growth ETF
Selecting the right large-cap growth ETF requires careful evaluation of individual financial goals and risk tolerance. Investors seeking long-term capital appreciation should prioritize ETFs with strong growth potential, while those focused on stability may prefer funds with lower volatility. Risk tolerance plays a crucial role, as large-cap growth ETFs tend to experience higher price fluctuations compared to value-oriented funds. Comparing fund objectives, expense ratios, and sector weightings is essential for making an informed decision. Sector weightings also vary. Liquidity and long-term investment outlook are additional factors to consider when choosing a large-cap growth ETF. Investors should analyze these differences to select an ETF that aligns with their investment preferences.
Conclusion
Large-cap growth ETFs provide investors with an efficient way to gain exposure to high-growth companies while maintaining diversification across key sectors. ETFs such as VUG, QQQ, and SCHG offer distinct advantages in terms of expense ratios, sector allocations, and historical performance, allowing investors to select funds that best align with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
While these ETFs benefit from strong returns during economic expansions, they also carry concentration risks due to their reliance on dominant stocks, particularly in the technology sector. Careful consideration of liquidity, expense ratios, and macroeconomic trends helps investors optimize their portfolios for long-term growth. By selecting the right large-cap growth ETF, investors can balance risk and reward while capitalizing on the potential of market-leading companies.