Introduction
Large-cap stocks play a crucial role in the financial markets, representing established companies with strong revenue streams and significant market influence. These stocks provide stability and long-term growth potential, making them a preferred choice for investors seeking reliable returns. Sector representation among large-cap companies varies widely, affecting portfolio diversification and investment strategies. Understanding how different sectors are weighted within large-cap indices helps investors balance risk and exposure across industries.
Understanding Large-Cap Sector Representation
Large-cap stocks are companies with a substantial market capitalization, typically exceeding $10 billion. These firms are well-established, financially stable, and often industry leaders. Their size and market influence make them attractive to investors seeking consistent returns and lower volatility compared to smaller companies. Large-cap stocks are commonly included in major indices such as the S&P 500 and Dow Jones Industrial Average, serving as benchmarks for market performance.
Sectors in large-cap indices are classified based on industry groupings, following frameworks such as the Global Industry Classification Standard (GICS). This system categorizes companies into sectors like technology, healthcare, financials, consumer goods, and energy. Each sector has distinct characteristics, with some offering higher growth potential while others provide stability through consistent earnings. Sector diversification is crucial in large-cap investing, as it reduces risk and enhances portfolio resilience.
Breakdown of Sector Weightings in Large-Cap Stocks
Sector weightings in large-cap benchmarks such as the S&P 500 and Dow Jones Industrial Average vary based on market trends and economic conditions. The S&P 500 is divided into 11 sectors, including technology, healthcare, financials, and consumer goods, with each sector contributing differently to the index’s overall composition. Technology is currently the largest sector, reflecting the dominance of companies like Apple and Microsoft. Comparing sector allocations across major indices reveals differences in market composition and investment focus.
The S&P 500 has a higher weighting in technology and healthcare, while the Dow Jones Industrial Average leans more toward industrials and consumer staples. Historical trends in sector representation show shifts in market leadership over time. Understanding these trends helps investors anticipate future market movements and adjust their sector allocations accordingly.
Technology Sector in Large-Caps
The technology sector has experienced significant growth within large-cap indices, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and semiconductor innovation. Companies like Microsoft, Apple, and Nvidia have expanded their market capitalization, reinforcing technology’s dominance in benchmarks such as the S&P 500 and Nasdaq-100. As digital transformation accelerates, technology stocks continue to shape global markets, attracting investors seeking both stability and high-growth potential.
Microsoft remains a top player due to its software ecosystem and cloud services. Apart from the well-established companies, other firms, such as Oracle, Salesforce, and Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing, also play critical roles in shaping sector weightings. As businesses integrate digital solutions, technology stocks remain central to large-cap indices, reinforcing their long-term investment appeal.
Healthcare Sector in Large-Caps
The healthcare sector holds a significant presence in large-cap indices, with pharmaceutical, biotech, and healthcare providers making up a substantial portion of market capitalization. Companies such as Eli Lilly, Johnson & Johnson, and UnitedHealth Group dominate the sector, contributing to its stability and growth. Pharmaceutical firms lead in market share due to their extensive research and development efforts, while biotech companies drive innovation in treatments and therapies. Major healthcare firms rank among the largest companies in global markets, reflecting their influence and financial strength.
Eli Lilly, for example, has a market capitalization exceeding $700 billion, making it one of the most valuable pharmaceutical companies. Regulatory changes and healthcare advancements continue to impact the sector’s performance and representation in large-cap rankings. Innovations in biotechnology, including AI-driven diagnostics and personalized medicine, drive growth and attract investor interest. The integration of digital health solutions and telemedicine further expands the sector’s reach.
Financial Sector in Large-Caps
The financial sector plays a crucial role in large-cap indices, with banks, asset management firms, and insurance companies ranking among the most influential stocks. Leading financial institutions such as JPMorgan Chase, Bank of America, and Goldman Sachs dominate the sector, contributing significantly to market capitalization. Financial institutions serve as a backbone for market stability, facilitating capital flow and economic growth. The financial sector’s stability is essential for maintaining investor confidence, as disruptions in banking or asset management can trigger broader market volatility. Interest rates and economic cycles significantly impact financial sector representation in large-cap indices.
Consumer Goods and Services in Large-Caps
The consumer goods and services sector in large-cap stocks is divided into two main categories: consumer discretionary and consumer staples. Consumer discretionary stocks include companies that provide non-essential goods and services, such as retail, entertainment, and luxury brands. Consumer staples stocks consist of businesses that offer essential products, including food, beverages, household goods, and personal care items. Key players in the consumer sector include multinational corporations with strong brand recognition and market influence.
In consumer staples, companies like Procter & Gamble, Coca-Cola, and Walmart dominate the industry, providing essential goods with consistent revenue streams. Consumer discretionary stocks feature major retailers such as Amazon, Nike, and Starbucks, which thrive on consumer spending trends. Several trends are shaping consumer-focused large-cap stocks, including digital transformation, sustainability initiatives, and shifting consumer preferences.
Energy Sector in Large-Caps
The energy sector holds a significant presence in large-cap indices, with oil, natural gas, and renewable energy firms shaping market dynamics. Leading companies such as Exxon Mobil, Chevron, and Shell dominate the sector, contributing to its overall weight in benchmarks like the S&P 500. Traditional fossil fuel companies maintain strong market positions due to global energy demand.
Commodity prices play a crucial role in determining sector weightings within large-cap indices. Oil and natural gas prices fluctuate based on geopolitical events, supply chain disruptions, and economic cycles, directly impacting the valuation of energy stocks. Sustainability trends are reshaping the energy sector’s representation in large-cap indices.
Industrials and Materials Sector in Large-Caps
The industrials and materials sector plays a vital role in large-cap indices, encompassing manufacturing, construction, and raw materials companies. Industrial firms produce machinery, equipment, and infrastructure essential for economic growth, while materials companies supply commodities such as metals, chemicals, and construction materials. Their presence in indices like the S&P 500 reflects their importance in global markets.
Major firms within the industrials sector include Caterpillar, Boeing, and Honeywell, which lead in manufacturing and aerospace technology. In the materials sector, companies such as Linde, Sherwin-Williams, and Southern Copper dominate, These firms maintain strong market positions due to their scale, technological advancements, and ability to adapt to changing economic conditions. Economic cycles significantly impact the composition of the industrials and materials sector.
Communication Services and Utilities in Large-Caps
The communication services and utilities sectors play distinct yet essential roles in large-cap indices, contributing to market stability and long-term investment opportunities. Telecom and media companies, including Alphabet, Meta Platforms, and Verizon, dominate the communication services sector, providing connectivity, digital content, and entertainment. These firms shape sector weightings in indices like the S&P 500, reflecting their influence on consumer behavior and technological advancements. Meanwhile, the utilities sector consists of companies such as NextEra Energy and Duke Energy, ensure steady revenue streams and defensive investment characteristics.
Utility sector weightings in large-cap indices remain relatively stable due to the industry's consistent demand and regulated pricing structures. Unlike cyclical sectors, utilities provide predictable cash flows, making them attractive to income-focused investors. Emerging trends in telecom, entertainment, and infrastructure investment are reshaping sector dynamics. Additionally, infrastructure investments in renewable energy and smart grids are modernizing the utilities sector.
Comparison of Sector Weightings Over Time
Sector weightings in large-cap indices have evolved over time, reflecting shifts in economic trends, technological advancements, and market dynamics. Historically, industries such as financials and energy held dominant positions in benchmarks like the S&P 500. However, the rise of technology and healthcare has reshaped sector allocations, with companies like Apple, Microsoft, and Eli Lilly gaining significant market share. Several factors contribute to sector growth or decline in large-cap rankings. Economic cycles play a crucial role. Additionally, regulatory changes, interest rate fluctuations, and geopolitical events affect sector performance. The increasing focus on sustainability has also impacted it.
Looking ahead, sector trends in large-cap investing are expected to continue evolving. Technology is likely to maintain its leadership position, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and cybersecurity. Healthcare will remain a key sector, benefiting from innovations in biotechnology and personalized medicine. Meanwhile, the energy sector may see further diversification, with renewable energy gaining prominence alongside traditional fossil fuels.
Investment Strategies Based on Sector Representation
Sector weightings play a crucial role in large-cap portfolio allocation, influencing risk exposure and return potential. Investors often adjust their sector allocations based on economic cycles, favoring defensive sectors like healthcare and consumer staples during downturns while increasing exposure to technology and financials during periods of growth. Diversifying across multiple sectors reduces risk while maintaining growth opportunities.
Sector-based strategies for dividend and growth investing cater to different investor preferences. Dividend-focused investors prioritize sectors with stable cash flows, such as utilities, consumer staples, and healthcare, which offer consistent payouts. Growth investors, on the other hand, seek sectors with high expansion potential, such as technology and communication services.
Conclusion
Sector representation in large-cap stocks impacts portfolio allocation, risk management, and investment strategies. Over time, evolving economic conditions and technological advancements have shifted sector weightings, with technology and healthcare gaining prominence. Investors can build diversified portfolios that balance stability and growth by understanding these trends.
Strategic sector allocation helps optimize returns and minimize volatility in response to changing market dynamics. A flexible investment approach is crucial for navigating future opportunities in large-cap investing.







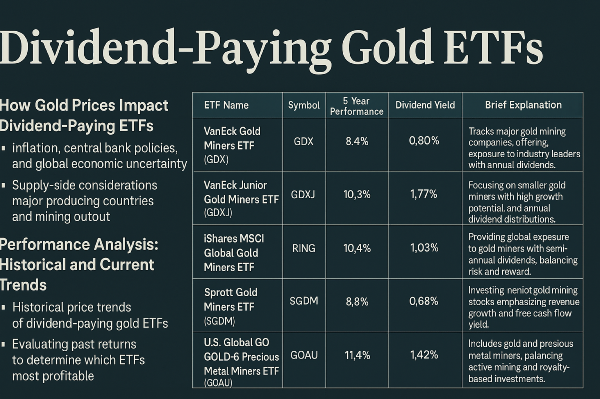

















Introduction
Large-cap stocks play a crucial role in the financial markets, representing established companies with strong revenue streams and significant market influence. These stocks provide stability and long-term growth potential, making them a preferred choice for investors seeking reliable returns. Sector representation among large-cap companies varies widely, affecting portfolio diversification and investment strategies. Understanding how different sectors are weighted within large-cap indices helps investors balance risk and exposure across industries.
Understanding Large-Cap Sector Representation
Large-cap stocks are companies with a substantial market capitalization, typically exceeding $10 billion. These firms are well-established, financially stable, and often industry leaders. Their size and market influence make them attractive to investors seeking consistent returns and lower volatility compared to smaller companies. Large-cap stocks are commonly included in major indices such as the S&P 500 and Dow Jones Industrial Average, serving as benchmarks for market performance.
Sectors in large-cap indices are classified based on industry groupings, following frameworks such as the Global Industry Classification Standard (GICS). This system categorizes companies into sectors like technology, healthcare, financials, consumer goods, and energy. Each sector has distinct characteristics, with some offering higher growth potential while others provide stability through consistent earnings. Sector diversification is crucial in large-cap investing, as it reduces risk and enhances portfolio resilience.
Breakdown of Sector Weightings in Large-Cap Stocks
Sector weightings in large-cap benchmarks such as the S&P 500 and Dow Jones Industrial Average vary based on market trends and economic conditions. The S&P 500 is divided into 11 sectors, including technology, healthcare, financials, and consumer goods, with each sector contributing differently to the index’s overall composition. Technology is currently the largest sector, reflecting the dominance of companies like Apple and Microsoft. Comparing sector allocations across major indices reveals differences in market composition and investment focus.
The S&P 500 has a higher weighting in technology and healthcare, while the Dow Jones Industrial Average leans more toward industrials and consumer staples. Historical trends in sector representation show shifts in market leadership over time. Understanding these trends helps investors anticipate future market movements and adjust their sector allocations accordingly.
Technology Sector in Large-Caps
The technology sector has experienced significant growth within large-cap indices, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and semiconductor innovation. Companies like Microsoft, Apple, and Nvidia have expanded their market capitalization, reinforcing technology’s dominance in benchmarks such as the S&P 500 and Nasdaq-100. As digital transformation accelerates, technology stocks continue to shape global markets, attracting investors seeking both stability and high-growth potential.
Microsoft remains a top player due to its software ecosystem and cloud services. Apart from the well-established companies, other firms, such as Oracle, Salesforce, and Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing, also play critical roles in shaping sector weightings. As businesses integrate digital solutions, technology stocks remain central to large-cap indices, reinforcing their long-term investment appeal.
Healthcare Sector in Large-Caps
The healthcare sector holds a significant presence in large-cap indices, with pharmaceutical, biotech, and healthcare providers making up a substantial portion of market capitalization. Companies such as Eli Lilly, Johnson & Johnson, and UnitedHealth Group dominate the sector, contributing to its stability and growth. Pharmaceutical firms lead in market share due to their extensive research and development efforts, while biotech companies drive innovation in treatments and therapies. Major healthcare firms rank among the largest companies in global markets, reflecting their influence and financial strength.
Eli Lilly, for example, has a market capitalization exceeding $700 billion, making it one of the most valuable pharmaceutical companies. Regulatory changes and healthcare advancements continue to impact the sector’s performance and representation in large-cap rankings. Innovations in biotechnology, including AI-driven diagnostics and personalized medicine, drive growth and attract investor interest. The integration of digital health solutions and telemedicine further expands the sector’s reach.
Financial Sector in Large-Caps
The financial sector plays a crucial role in large-cap indices, with banks, asset management firms, and insurance companies ranking among the most influential stocks. Leading financial institutions such as JPMorgan Chase, Bank of America, and Goldman Sachs dominate the sector, contributing significantly to market capitalization. Financial institutions serve as a backbone for market stability, facilitating capital flow and economic growth. The financial sector’s stability is essential for maintaining investor confidence, as disruptions in banking or asset management can trigger broader market volatility. Interest rates and economic cycles significantly impact financial sector representation in large-cap indices.
Consumer Goods and Services in Large-Caps
The consumer goods and services sector in large-cap stocks is divided into two main categories: consumer discretionary and consumer staples. Consumer discretionary stocks include companies that provide non-essential goods and services, such as retail, entertainment, and luxury brands. Consumer staples stocks consist of businesses that offer essential products, including food, beverages, household goods, and personal care items. Key players in the consumer sector include multinational corporations with strong brand recognition and market influence.
In consumer staples, companies like Procter & Gamble, Coca-Cola, and Walmart dominate the industry, providing essential goods with consistent revenue streams. Consumer discretionary stocks feature major retailers such as Amazon, Nike, and Starbucks, which thrive on consumer spending trends. Several trends are shaping consumer-focused large-cap stocks, including digital transformation, sustainability initiatives, and shifting consumer preferences.
Energy Sector in Large-Caps
The energy sector holds a significant presence in large-cap indices, with oil, natural gas, and renewable energy firms shaping market dynamics. Leading companies such as Exxon Mobil, Chevron, and Shell dominate the sector, contributing to its overall weight in benchmarks like the S&P 500. Traditional fossil fuel companies maintain strong market positions due to global energy demand.
Commodity prices play a crucial role in determining sector weightings within large-cap indices. Oil and natural gas prices fluctuate based on geopolitical events, supply chain disruptions, and economic cycles, directly impacting the valuation of energy stocks. Sustainability trends are reshaping the energy sector’s representation in large-cap indices.
Industrials and Materials Sector in Large-Caps
The industrials and materials sector plays a vital role in large-cap indices, encompassing manufacturing, construction, and raw materials companies. Industrial firms produce machinery, equipment, and infrastructure essential for economic growth, while materials companies supply commodities such as metals, chemicals, and construction materials. Their presence in indices like the S&P 500 reflects their importance in global markets.
Major firms within the industrials sector include Caterpillar, Boeing, and Honeywell, which lead in manufacturing and aerospace technology. In the materials sector, companies such as Linde, Sherwin-Williams, and Southern Copper dominate, These firms maintain strong market positions due to their scale, technological advancements, and ability to adapt to changing economic conditions. Economic cycles significantly impact the composition of the industrials and materials sector.
Communication Services and Utilities in Large-Caps
The communication services and utilities sectors play distinct yet essential roles in large-cap indices, contributing to market stability and long-term investment opportunities. Telecom and media companies, including Alphabet, Meta Platforms, and Verizon, dominate the communication services sector, providing connectivity, digital content, and entertainment. These firms shape sector weightings in indices like the S&P 500, reflecting their influence on consumer behavior and technological advancements. Meanwhile, the utilities sector consists of companies such as NextEra Energy and Duke Energy, ensure steady revenue streams and defensive investment characteristics.
Utility sector weightings in large-cap indices remain relatively stable due to the industry's consistent demand and regulated pricing structures. Unlike cyclical sectors, utilities provide predictable cash flows, making them attractive to income-focused investors. Emerging trends in telecom, entertainment, and infrastructure investment are reshaping sector dynamics. Additionally, infrastructure investments in renewable energy and smart grids are modernizing the utilities sector.
Comparison of Sector Weightings Over Time
Sector weightings in large-cap indices have evolved over time, reflecting shifts in economic trends, technological advancements, and market dynamics. Historically, industries such as financials and energy held dominant positions in benchmarks like the S&P 500. However, the rise of technology and healthcare has reshaped sector allocations, with companies like Apple, Microsoft, and Eli Lilly gaining significant market share. Several factors contribute to sector growth or decline in large-cap rankings. Economic cycles play a crucial role. Additionally, regulatory changes, interest rate fluctuations, and geopolitical events affect sector performance. The increasing focus on sustainability has also impacted it.
Looking ahead, sector trends in large-cap investing are expected to continue evolving. Technology is likely to maintain its leadership position, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and cybersecurity. Healthcare will remain a key sector, benefiting from innovations in biotechnology and personalized medicine. Meanwhile, the energy sector may see further diversification, with renewable energy gaining prominence alongside traditional fossil fuels.
Investment Strategies Based on Sector Representation
Sector weightings play a crucial role in large-cap portfolio allocation, influencing risk exposure and return potential. Investors often adjust their sector allocations based on economic cycles, favoring defensive sectors like healthcare and consumer staples during downturns while increasing exposure to technology and financials during periods of growth. Diversifying across multiple sectors reduces risk while maintaining growth opportunities.
Sector-based strategies for dividend and growth investing cater to different investor preferences. Dividend-focused investors prioritize sectors with stable cash flows, such as utilities, consumer staples, and healthcare, which offer consistent payouts. Growth investors, on the other hand, seek sectors with high expansion potential, such as technology and communication services.
Conclusion
Sector representation in large-cap stocks impacts portfolio allocation, risk management, and investment strategies. Over time, evolving economic conditions and technological advancements have shifted sector weightings, with technology and healthcare gaining prominence. Investors can build diversified portfolios that balance stability and growth by understanding these trends.
Strategic sector allocation helps optimize returns and minimize volatility in response to changing market dynamics. A flexible investment approach is crucial for navigating future opportunities in large-cap investing.