Introduction
International large-cap ETFs provide investors with access to globally recognized companies that drive economic growth across various sectors and regions. Many seek international large-cap exposure to balance risk, capitalize on emerging trends, and enhance portfolio stability. This article explores the characteristics of large-cap international ETFs, evaluates key selection criteria, highlights top-performing funds, and examines strategies for integrating them into a diversified investment portfolio.
Defining Large-Cap International ETFs
Large-cap stocks represent well-established companies with substantial market capitalization, typically exceeding billions of dollars. These firms often have strong financial stability, consistent revenue streams, and a dominant presence in their industries. Large-cap international ETFs provide investors with diversified exposure to these global corporations, allowing them to participate in economic growth across multiple regions. International large-cap ETFs differ from domestic ETFs in several ways.
While domestic ETFs focus on companies within a single country, international ETFs include firms from various global markets. This broader exposure helps investors mitigate risks associated with economic downturns in any one region. Investing in large-cap international ETFs offers several benefits, including diversification and access to global industry leaders.
Key Criteria for Evaluating International Large-Cap ETFs
Evaluating international large-cap ETFs requires analyzing key performance metrics, including historical returns and volatility. Investors should assess how an ETF has performed over different market cycles to gauge its resilience during downturns and growth periods. Volatility measures the degree of price fluctuations, helping investors determine risk levels. Compare an ETF’s performance against relevant benchmarks, such as the MSCI World Index. Expense ratios and fund costs are critical factors in selecting an ETF.
Lower expense ratios allow investors to retain more of their returns over time. While passive ETFs generally have lower fees, actively managed funds may justify higher costs through strategic stock selection and risk management. Sector and geographic diversification influence an ETF’s risk exposure and growth potential. Some funds focus on developed markets, while others include emerging economies with higher volatility but greater upside potential. Sector allocations vary, with certain ETFs emphasizing technology, financials, or consumer goods.
Top International Large-Cap ETFs
Large-cap international ETFs provide investors with exposure to well-established companies across global markets. These funds track indices that include multinational corporations from developed and emerging economies, offering diversification beyond domestic investments. Some of the most popular large-cap international ETFs include the iShares Core MSCI Total International Stock ETF (IXUS), Vanguard Total International Stock ETF (VXUS), and iShares MSCI EAFE Growth ETF (EFG). When comparing large-cap international ETFs, investors should consider key performance metrics, expense ratios, and sector allocations.
IXUS provides broad exposure to international markets, including both developed and emerging economies, while VXUS focuses primarily on developed markets. Expense ratios vary among funds, with Vanguard ETFs typically offering lower costs compared to actively managed alternatives. Additionally, liquidity and trading volume should be considered, as higher liquidity ensures smoother transactions and minimizes price discrepancies.
Regional Considerations in Large-Cap International ETFs
Large-cap international ETFs vary in their focus on developed and emerging markets. ETFs targeting developed markets, such as those tracking the MSCI EAFE Index, provide exposure to stable economies like Europe, Japan, and Australia. These funds tend to have lower volatility and include well-established multinational corporations. In contrast, ETFs focused on emerging markets, such as those tracking the MSCI Emerging Markets Index, invest in countries with high growth potential, such as China and India.
Sector allocations differ across regions, influencing ETF performance. Developed market ETFs often have higher exposure to industries such as financial services, healthcare, and consumer goods, reflecting the stability of these economies. Emerging market ETFs, on the other hand, may emphasize technology, industrials, and commodities. Economic and regulatory trends play a crucial role in shaping the performance of large-cap international ETFs.
Risk Factors Associated with International Large-Cap ETFs
Currency fluctuations and foreign exchange risk are key concerns when investing in international large-cap ETFs. Since these funds hold assets denominated in foreign currencies, shifts in exchange rates can impact returns. Some ETFs offer currency-hedged options to mitigate this risk, but they often come with higher expense ratios. Political events, trade disputes, and economic downturns in specific regions can lead to market volatility. Market correlation and downturns pose another challenge for international ETF investors. While diversification helps mitigate risk, global markets are often interconnected. Varying tax policies, reporting standards, and market regulations may create complexities for investors seeking international exposure.
Tax Implications of Investing in International ETFs
Taxation on international ETFs differs from domestic investments due to varying regulations across countries. Investors holding foreign assets may be subject to both U.S. income tax and taxes imposed by the country where the ETF is domiciled. Some nations have no capital gains tax, while others levy taxes on dividends and interest earned from international holdings. To mitigate double taxation, the U.S. offers a foreign tax credit. Many countries impose a withholding tax on dividends paid to foreign investors, reducing the net income received. Tax-efficient investing in global ETFs requires careful planning. Additionally, holding international ETFs in tax-advantaged accounts, such as IRAs, can help reduce taxable income.
Strategies for Selecting the Best International Large-Cap ETF
Selecting the best international large-cap ETF requires aligning investment choices with financial goals and risk tolerance. Evaluating an ETF’s historical performance, sector allocation, and volatility can help determine whether it fits an investor’s strategy. Additionally, considering factors such as dividend yield and expense ratios ensures a well-rounded selection process.
Combining international ETFs with domestic funds can enhance portfolio balance. A diversified approach allows investors to mitigate risks associated with economic downturns in specific regions while capitalizing on global growth opportunities. Some investors use a core-and-satellite strategy, where broad-market ETFs form the foundation, complemented by region-specific funds. Investors must also decide between active and passive investment approaches when selecting an international large-cap ETF. Passive ETFs track established indices, offering low-cost exposure to broad markets with minimal management intervention.
Future Trends in Large-Cap International ETFs
Emerging markets are expected to play a growing role in large-cap investing as economies in regions such as Asia and Latin America continue to expand. ETFs that include large-cap stocks from these markets provide investors with exposure to companies benefiting from rapid industrialization and technological advancements. As global trade evolves, emerging markets may contribute significantly to international ETF performance.
Shifting economic dynamics are influencing the performance of large-cap international ETFs. Factors such as inflation rates, interest rate policies, geopolitical events and regulatory changes impact global markets, leading to fluctuations in ETF valuations. Innovations in artificial intelligence, renewable energy, and digital infrastructure are driving growth in various sectors, influencing ETF compositions.
Conclusion
International large-cap ETFs serve as a vital tool for investors seeking global diversification, stability, and long-term growth potential. By offering access to established multinational corporations across various economies, these funds help mitigate regional risks while capitalizing on emerging opportunities. Selecting the best ETF involves evaluating performance metrics, expense ratios, sector allocations, and macroeconomic trends.
As global markets evolve, technological advancements and economic shifts will continue shaping the composition and returns of these ETFs. Investors who strategically integrate international large-cap ETFs into their portfolios can position themselves for sustained success in an increasingly interconnected financial landscape.


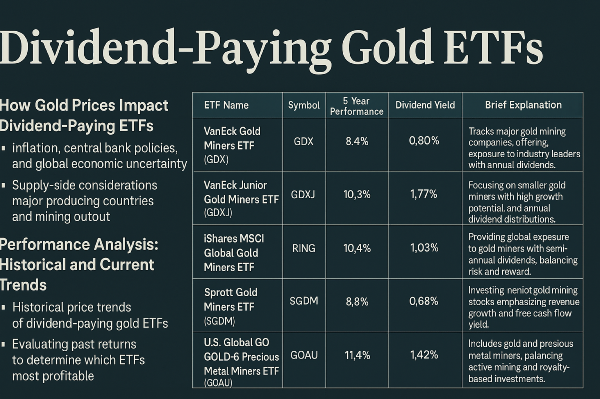
















Introduction International large-cap ETFs provide investors with access to globally recognized companies that drive economic growth across various sectors and regions. Many seek international large-cap exposure to balance risk, capitalize on emerging trends, and enhance portfolio stability. This article explores the characteristics of large-cap international ETFs, evaluates key selection criteria, highlights top-performing funds, and examines strategies for integrating them into a diversified investment portfolio.
Defining Large-Cap International ETFs
Large-cap stocks represent well-established companies with substantial market capitalization, typically exceeding billions of dollars. These firms often have strong financial stability, consistent revenue streams, and a dominant presence in their industries. Large-cap international ETFs provide investors with diversified exposure to these global corporations, allowing them to participate in economic growth across multiple regions. International large-cap ETFs differ from domestic ETFs in several ways.
While domestic ETFs focus on companies within a single country, international ETFs include firms from various global markets. This broader exposure helps investors mitigate risks associated with economic downturns in any one region. Investing in large-cap international ETFs offers several benefits, including diversification and access to global industry leaders.
Key Criteria for Evaluating International Large-Cap ETFs
Evaluating international large-cap ETFs requires analyzing key performance metrics, including historical returns and volatility. Investors should assess how an ETF has performed over different market cycles to gauge its resilience during downturns and growth periods. Volatility measures the degree of price fluctuations, helping investors determine risk levels. Compare an ETF’s performance against relevant benchmarks, such as the MSCI World Index. Expense ratios and fund costs are critical factors in selecting an ETF.
Lower expense ratios allow investors to retain more of their returns over time. While passive ETFs generally have lower fees, actively managed funds may justify higher costs through strategic stock selection and risk management. Sector and geographic diversification influence an ETF’s risk exposure and growth potential. Some funds focus on developed markets, while others include emerging economies with higher volatility but greater upside potential. Sector allocations vary, with certain ETFs emphasizing technology, financials, or consumer goods.
Top International Large-Cap ETFs
Large-cap international ETFs provide investors with exposure to well-established companies across global markets. These funds track indices that include multinational corporations from developed and emerging economies, offering diversification beyond domestic investments. Some of the most popular large-cap international ETFs include the iShares Core MSCI Total International Stock ETF (IXUS), Vanguard Total International Stock ETF (VXUS), and iShares MSCI EAFE Growth ETF (EFG). When comparing large-cap international ETFs, investors should consider key performance metrics, expense ratios, and sector allocations.
IXUS provides broad exposure to international markets, including both developed and emerging economies, while VXUS focuses primarily on developed markets. Expense ratios vary among funds, with Vanguard ETFs typically offering lower costs compared to actively managed alternatives. Additionally, liquidity and trading volume should be considered, as higher liquidity ensures smoother transactions and minimizes price discrepancies.
Regional Considerations in Large-Cap International ETFs
Large-cap international ETFs vary in their focus on developed and emerging markets. ETFs targeting developed markets, such as those tracking the MSCI EAFE Index, provide exposure to stable economies like Europe, Japan, and Australia. These funds tend to have lower volatility and include well-established multinational corporations. In contrast, ETFs focused on emerging markets, such as those tracking the MSCI Emerging Markets Index, invest in countries with high growth potential, such as China and India.
Sector allocations differ across regions, influencing ETF performance. Developed market ETFs often have higher exposure to industries such as financial services, healthcare, and consumer goods, reflecting the stability of these economies. Emerging market ETFs, on the other hand, may emphasize technology, industrials, and commodities. Economic and regulatory trends play a crucial role in shaping the performance of large-cap international ETFs.
Risk Factors Associated with International Large-Cap ETFs
Currency fluctuations and foreign exchange risk are key concerns when investing in international large-cap ETFs. Since these funds hold assets denominated in foreign currencies, shifts in exchange rates can impact returns. Some ETFs offer currency-hedged options to mitigate this risk, but they often come with higher expense ratios. Political events, trade disputes, and economic downturns in specific regions can lead to market volatility. Market correlation and downturns pose another challenge for international ETF investors. While diversification helps mitigate risk, global markets are often interconnected. Varying tax policies, reporting standards, and market regulations may create complexities for investors seeking international exposure.
Tax Implications of Investing in International ETFs
Taxation on international ETFs differs from domestic investments due to varying regulations across countries. Investors holding foreign assets may be subject to both U.S. income tax and taxes imposed by the country where the ETF is domiciled. Some nations have no capital gains tax, while others levy taxes on dividends and interest earned from international holdings. To mitigate double taxation, the U.S. offers a foreign tax credit. Many countries impose a withholding tax on dividends paid to foreign investors, reducing the net income received. Tax-efficient investing in global ETFs requires careful planning. Additionally, holding international ETFs in tax-advantaged accounts, such as IRAs, can help reduce taxable income.
Strategies for Selecting the Best International Large-Cap ETF
Selecting the best international large-cap ETF requires aligning investment choices with financial goals and risk tolerance. Evaluating an ETF’s historical performance, sector allocation, and volatility can help determine whether it fits an investor’s strategy. Additionally, considering factors such as dividend yield and expense ratios ensures a well-rounded selection process.
Combining international ETFs with domestic funds can enhance portfolio balance. A diversified approach allows investors to mitigate risks associated with economic downturns in specific regions while capitalizing on global growth opportunities. Some investors use a core-and-satellite strategy, where broad-market ETFs form the foundation, complemented by region-specific funds. Investors must also decide between active and passive investment approaches when selecting an international large-cap ETF. Passive ETFs track established indices, offering low-cost exposure to broad markets with minimal management intervention.
Future Trends in Large-Cap International ETFs
Emerging markets are expected to play a growing role in large-cap investing as economies in regions such as Asia and Latin America continue to expand. ETFs that include large-cap stocks from these markets provide investors with exposure to companies benefiting from rapid industrialization and technological advancements. As global trade evolves, emerging markets may contribute significantly to international ETF performance.
Shifting economic dynamics are influencing the performance of large-cap international ETFs. Factors such as inflation rates, interest rate policies, geopolitical events and regulatory changes impact global markets, leading to fluctuations in ETF valuations. Innovations in artificial intelligence, renewable energy, and digital infrastructure are driving growth in various sectors, influencing ETF compositions.
Conclusion
International large-cap ETFs serve as a vital tool for investors seeking global diversification, stability, and long-term growth potential. By offering access to established multinational corporations across various economies, these funds help mitigate regional risks while capitalizing on emerging opportunities. Selecting the best ETF involves evaluating performance metrics, expense ratios, sector allocations, and macroeconomic trends.
As global markets evolve, technological advancements and economic shifts will continue shaping the composition and returns of these ETFs. Investors who strategically integrate international large-cap ETFs into their portfolios can position themselves for sustained success in an increasingly interconnected financial landscape.