Introduction
The S&P 500 is a widely recognized stock market index that tracks the performance of 500 of the largest publicly traded companies in the United States. It serves as a key benchmark for investors, reflecting overall market trends and economic health. Many perceive the S&P 500 as an exclusively large-cap index, given its focus on established corporations with significant market capitalization. However, while the majority of its constituents are large-cap stocks, periodic rebalancing may introduce mid-cap companies, influencing its composition. As a result, the index remains a vital tool for assessing market stability and guiding investment strategies.
Composition of the S&P 500
The S&P 500 consists of 500 publicly traded companies selected based on specific criteria, including market capitalization, liquidity, and financial stability. Companies such as Microsoft and Apple meet these requirements due to their strong earnings and consistent market presence. To be included, a company must have a market capitalization of at least $14.6 billion, be U.S.-based, and maintain a high trading volume. The index is periodically rebalanced to ensure it reflects the evolving market landscape.
Market capitalization plays a crucial role in determining the composition of the S&P 500. While the index primarily consists of large-cap stocks, it occasionally includes mid-cap companies that meet the eligibility criteria. Firms such as Tesla and Nvidia have transitioned from mid-cap to large-cap status due to rapid growth. The index serves as a benchmark for investors, offering exposure to a diverse range of industries, including technology, healthcare, and finance.
Despite its large-cap focus, the S&P 500 does not exclusively contain large-cap stocks. Some mid-cap companies are included based on market fluctuations and index adjustments. Financial institutions such as JPMorgan Chase and Bank of America represent the financial sector, while consumer-focused firms like Walmart contribute to retail stability. Investors rely on the S&P 500 for diversified exposure, balancing growth potential with market resilience.
Sources
SlickCharts
Stock Analysis
Top Foreign Stocks
Are All Companies in the S&P 500 Large-Cap?
The S&P 500 is widely regarded as a large-cap index, but it occasionally includes mid-cap companies that meet its selection criteria. While most of its constituents are large-cap stocks, some firms transition between mid-cap and large-cap status due to market fluctuations. Companies such as Tesla and Nvidia have experienced rapid growth, elevating them from mid-cap to large-cap classification. The index is periodically rebalanced to reflect market dynamics, ensuring that it remains representative of the broader economy.
Several factors influence company classification within the S&P 500, including market capitalization, liquidity, and financial stability. Firms such as JPMorgan Chase and Bank of America maintain large-cap status due to their consistent earnings and institutional investment. However, mid-cap companies that demonstrate strong financial performance may be added to the index, expanding its composition beyond strictly large-cap stocks. Investors should consider these classification shifts when analyzing index fund investments and market trends.
Sources
Stock Analysis
Wikipedia
SlickCharts
Comparison Between the S&P 500 and Other Market Indices
The S&P 500, Russell 1000, and Dow Jones Industrial Average each serve distinct roles in financial markets, influencing investment strategies based on their composition. The S&P 500 tracks 500 of the largest publicly traded U.S. companies, including Microsoft and Apple, offering broad exposure to large-cap stocks. The Russell 1000 encompasses a wider range of companies, including mid-cap stocks, providing a more comprehensive view of market performance. The Dow Jones Industrial Average, in contrast, consists of only 30 blue-chip companies, such as JPMorgan Chase, making it a more concentrated index focused on industry leaders.
Index composition significantly impacts investment strategies, as each index reflects different levels of diversification and risk exposure. The S&P 500 is market-cap weighted, meaning larger companies like Amazon and Alphabet have a greater influence on its performance. The Russell 1000, with its inclusion of mid-cap stocks, offers investors a balance between stability and growth potential. The Dow Jones, being price-weighted, gives higher-priced stocks more influence, which can lead to greater volatility in response to individual stock movements.
Investors choose between these indices based on their financial goals and risk tolerance. The S&P 500 is favored for long-term growth and diversification, while the Russell 1000 provides exposure to a broader range of companies, including emerging mid-cap firms. The Dow Jones, with its focus on established industry leaders, appeals to investors seeking stability and defensive positioning. Understanding these differences allows investors to tailor their portfolios to align with market trends and economic conditions.
Sources
Investopedia
The Balance
SmartAsset
Investment Strategies for S&P 500 Funds
Passive and active investment approaches offer distinct strategies for investing in S&P 500 funds. Passive investing involves tracking the index through exchange-traded funds (ETFs) or mutual funds, such as those holding Microsoft and Apple. This strategy minimizes fees and trading activity, making it cost-effective for long-term investors. Active investing, on the other hand, relies on fund managers to select stocks and adjust portfolios to outperform the index. While active funds may achieve higher returns, they often come with increased fees and market timing risks.
S&P 500 index funds provide several benefits, including diversification, lower costs, and historical stability. Companies such as Amazon and Alphabet contribute to index fund performance, ensuring exposure to industry leaders. However, risks include market downturns and limited flexibility in stock selection. Since index funds mirror the market, they cannot pivot to avoid underperforming sectors or capitalize on emerging opportunities. Investors must weigh these factors when choosing between passive and active strategies.
Portfolio diversification is a key consideration when investing in S&P 500 funds. Financial institutions such as JPMorgan Chase and Bank of America provide stability, while technology firms drive growth. Investors seeking balanced portfolios may combine S&P 500 funds with mid-cap or international stocks to enhance diversification. Understanding market trends and sector-specific risks allows investors to optimize their strategies for long-term success.
Sources
Forbes
NerdWallet
Times Money Mentor
Market Trends and Future Outlook for the S&P 500
The S&P 500 is expected to experience gradual composition shifts as market dynamics evolve. Companies such as Microsoft and Apple continue to anchor the index, but emerging mid-cap firms may gain inclusion due to growth trends. Analysts predict that technology and healthcare sectors will drive future index adjustments, reflecting broader economic shifts. As institutional investors allocate more capital to passive funds, the S&P 500 is likely to maintain its role as a dominant benchmark for market performance.
Despite its stability, the S&P 500 faces emerging risks, including inflation concerns and regulatory changes. Companies such as Amazon and Alphabet are subject to evolving policies that may impact stock valuations. Additionally, geopolitical tensions and trade policies could introduce volatility, affecting investor sentiment. However, opportunities remain in sectors poised for long-term growth, such as artificial intelligence and sustainable energy, which may influence future index composition.
Sources
Benzinga
Morgan Stanley
Norada Real Estate
Conclusion
The S&P 500 remains a cornerstone of financial markets, offering investors diversified exposure to industry-leading companies. While primarily composed of large-cap stocks, periodic rebalancing introduces mid-cap firms, ensuring representation of evolving market trends. As passive investing grows, the index continues to serve as a benchmark for stability and long-term portfolio strategy. Understanding its composition, investment approaches, and emerging market dynamics enables investors to make informed decisions and optimize their financial strategies in an ever-changing economic landscape.
📌Read More About:
The Top Large Cap Stocks- https://stockbossup.com/pages/topics/large-cap


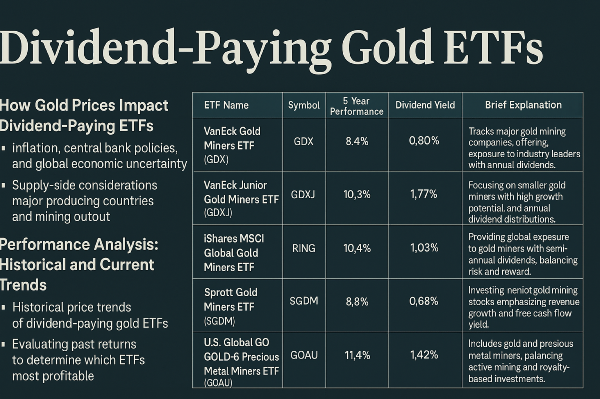
























Introduction
The S&P 500 is a widely recognized stock market index that tracks the performance of 500 of the largest publicly traded companies in the United States. It serves as a key benchmark for investors, reflecting overall market trends and economic health. Many perceive the S&P 500 as an exclusively large-cap index, given its focus on established corporations with significant market capitalization. However, while the majority of its constituents are large-cap stocks, periodic rebalancing may introduce mid-cap companies, influencing its composition. As a result, the index remains a vital tool for assessing market stability and guiding investment strategies.
Composition of the S&P 500
The S&P 500 consists of 500 publicly traded companies selected based on specific criteria, including market capitalization, liquidity, and financial stability. Companies such as Microsoft and Apple meet these requirements due to their strong earnings and consistent market presence. To be included, a company must have a market capitalization of at least $14.6 billion, be U.S.-based, and maintain a high trading volume. The index is periodically rebalanced to ensure it reflects the evolving market landscape.
Market capitalization plays a crucial role in determining the composition of the S&P 500. While the index primarily consists of large-cap stocks, it occasionally includes mid-cap companies that meet the eligibility criteria. Firms such as Tesla and Nvidia have transitioned from mid-cap to large-cap status due to rapid growth. The index serves as a benchmark for investors, offering exposure to a diverse range of industries, including technology, healthcare, and finance.
Despite its large-cap focus, the S&P 500 does not exclusively contain large-cap stocks. Some mid-cap companies are included based on market fluctuations and index adjustments. Financial institutions such as JPMorgan Chase and Bank of America represent the financial sector, while consumer-focused firms like Walmart contribute to retail stability. Investors rely on the S&P 500 for diversified exposure, balancing growth potential with market resilience.
Sources
SlickCharts
Stock Analysis
Top Foreign Stocks
Are All Companies in the S&P 500 Large-Cap?
The S&P 500 is widely regarded as a large-cap index, but it occasionally includes mid-cap companies that meet its selection criteria. While most of its constituents are large-cap stocks, some firms transition between mid-cap and large-cap status due to market fluctuations. Companies such as Tesla and Nvidia have experienced rapid growth, elevating them from mid-cap to large-cap classification. The index is periodically rebalanced to reflect market dynamics, ensuring that it remains representative of the broader economy.
Several factors influence company classification within the S&P 500, including market capitalization, liquidity, and financial stability. Firms such as JPMorgan Chase and Bank of America maintain large-cap status due to their consistent earnings and institutional investment. However, mid-cap companies that demonstrate strong financial performance may be added to the index, expanding its composition beyond strictly large-cap stocks. Investors should consider these classification shifts when analyzing index fund investments and market trends.
Sources
Stock Analysis
Wikipedia
SlickCharts
Comparison Between the S&P 500 and Other Market Indices
The S&P 500, Russell 1000, and Dow Jones Industrial Average each serve distinct roles in financial markets, influencing investment strategies based on their composition. The S&P 500 tracks 500 of the largest publicly traded U.S. companies, including Microsoft and Apple, offering broad exposure to large-cap stocks. The Russell 1000 encompasses a wider range of companies, including mid-cap stocks, providing a more comprehensive view of market performance. The Dow Jones Industrial Average, in contrast, consists of only 30 blue-chip companies, such as JPMorgan Chase, making it a more concentrated index focused on industry leaders.
Index composition significantly impacts investment strategies, as each index reflects different levels of diversification and risk exposure. The S&P 500 is market-cap weighted, meaning larger companies like Amazon and Alphabet have a greater influence on its performance. The Russell 1000, with its inclusion of mid-cap stocks, offers investors a balance between stability and growth potential. The Dow Jones, being price-weighted, gives higher-priced stocks more influence, which can lead to greater volatility in response to individual stock movements.
Investors choose between these indices based on their financial goals and risk tolerance. The S&P 500 is favored for long-term growth and diversification, while the Russell 1000 provides exposure to a broader range of companies, including emerging mid-cap firms. The Dow Jones, with its focus on established industry leaders, appeals to investors seeking stability and defensive positioning. Understanding these differences allows investors to tailor their portfolios to align with market trends and economic conditions.
Sources
Investopedia
The Balance
SmartAsset
Investment Strategies for S&P 500 Funds
Passive and active investment approaches offer distinct strategies for investing in S&P 500 funds. Passive investing involves tracking the index through exchange-traded funds (ETFs) or mutual funds, such as those holding Microsoft and Apple. This strategy minimizes fees and trading activity, making it cost-effective for long-term investors. Active investing, on the other hand, relies on fund managers to select stocks and adjust portfolios to outperform the index. While active funds may achieve higher returns, they often come with increased fees and market timing risks.
S&P 500 index funds provide several benefits, including diversification, lower costs, and historical stability. Companies such as Amazon and Alphabet contribute to index fund performance, ensuring exposure to industry leaders. However, risks include market downturns and limited flexibility in stock selection. Since index funds mirror the market, they cannot pivot to avoid underperforming sectors or capitalize on emerging opportunities. Investors must weigh these factors when choosing between passive and active strategies.
Portfolio diversification is a key consideration when investing in S&P 500 funds. Financial institutions such as JPMorgan Chase and Bank of America provide stability, while technology firms drive growth. Investors seeking balanced portfolios may combine S&P 500 funds with mid-cap or international stocks to enhance diversification. Understanding market trends and sector-specific risks allows investors to optimize their strategies for long-term success.
Sources
Forbes
NerdWallet
Times Money Mentor
Market Trends and Future Outlook for the S&P 500
The S&P 500 is expected to experience gradual composition shifts as market dynamics evolve. Companies such as Microsoft and Apple continue to anchor the index, but emerging mid-cap firms may gain inclusion due to growth trends. Analysts predict that technology and healthcare sectors will drive future index adjustments, reflecting broader economic shifts. As institutional investors allocate more capital to passive funds, the S&P 500 is likely to maintain its role as a dominant benchmark for market performance.
Despite its stability, the S&P 500 faces emerging risks, including inflation concerns and regulatory changes. Companies such as Amazon and Alphabet are subject to evolving policies that may impact stock valuations. Additionally, geopolitical tensions and trade policies could introduce volatility, affecting investor sentiment. However, opportunities remain in sectors poised for long-term growth, such as artificial intelligence and sustainable energy, which may influence future index composition.
Sources
Benzinga Morgan Stanley
Norada Real Estate
Conclusion
The S&P 500 remains a cornerstone of financial markets, offering investors diversified exposure to industry-leading companies. While primarily composed of large-cap stocks, periodic rebalancing introduces mid-cap firms, ensuring representation of evolving market trends. As passive investing grows, the index continues to serve as a benchmark for stability and long-term portfolio strategy. Understanding its composition, investment approaches, and emerging market dynamics enables investors to make informed decisions and optimize their financial strategies in an ever-changing economic landscape.
📌Read More About:
The Top Large Cap Stocks- https://stockbossup.com/pages/topics/large-cap