Introduction
Large-cap S&P 500 ETFs provide investors with diversified exposure to the largest publicly traded companies in the United States. These funds track the S&P 500 index, ensuring broad market representation and stability in portfolio management. Selecting the best ETF requires evaluating key factors such as expense ratios, liquidity, sector allocations, and historical performance. Since the S&P 500 covers approximately 80% of the U.S. stock market by capitalization, investing in these ETFs allows individuals to participate in the growth of industry leaders while minimizing individual stock risk. Understanding these elements helps investors optimize their portfolios for long-term success.
Understanding Large-Cap S&P 500 ETFs
Large-cap S&P 500 ETFs are exchange-traded funds designed to track the performance of the S&P 500 index, which consists of the 500 largest publicly traded companies in the United States. These ETFs provide investors with broad market exposure, ensuring diversification across multiple sectors. Since they mirror the index’s composition, large-cap S&P 500 ETFs offer a straightforward way to invest in industry-leading companies without the need for individual stock selection.
Their passive management structure allows them to maintain low expense ratios, making them cost-effective investment options for long-term growth. These ETFs differ from other index funds and actively managed funds in multiple ways. Investing in large-cap S&P 500 ETFs offers several advantages, particularly for long-term investors. These funds provide stability by including well-established companies with strong financial positions, reducing overall portfolio risk.
Top Large-Cap S&P 500 ETFs in the Market
Large-cap S&P 500 ETFs such as SPY, VOO, and IVV are among the most widely traded funds, offering investors exposure to the largest companies in the U.S. stock market. SPY, managed by State Street Global Advisors, is the oldest and most liquid S&P 500 ETF, making it a preferred choice for traders. VOO, issued by Vanguard, and IVV, managed by iShares, provide similar exposure but with lower expense ratios, making them attractive for long-term investors. These ETFs track the S&P 500 index, ensuring broad diversification across multiple sectors while maintaining a focus on industry leaders.
Comparing the holdings and expense ratios of these ETFs reveals key differences. Despite tracking the same index, slight variations in fund structure and trading spreads can impact returns. The top holdings in these ETFs include mega-cap stocks such as Apple, Microsoft, and Amazon, which collectively account for a significant portion of the fund’s weightings. Sector distribution within SPY, VOO, and IVV highlights the dominance of technology, healthcare, and financial stocks. The concentration of mega-cap stocks within these ETFs can lead to higher volatility, particularly when leading companies experience price swings.
Performance Analysis of Large-Cap S&P 500 ETFs
Large-cap S&P 500 ETFs have historically delivered strong returns, closely mirroring the performance of the broader market. Funds such as SPY, VOO, and IVV have demonstrated consistent growth over the years, benefiting from the stability of large-cap stocks. However, these ETFs also experience volatility during market downturns, as they are directly influenced by macroeconomic conditions.
Investors should consider historical return trends alongside risk tolerance when selecting an S&P 500 ETF. Economic cycles play a crucial role in shaping the performance of large-cap S&P 500 ETFs. The long-term sustainability of index tracking remains a key advantage of large-cap S&P 500 ETFs. While short-term volatility may impact returns, the long-term trajectory of these ETFs remains positive, making them reliable options for wealth accumulation.
Expense Ratios and Cost Considerations
Low expense ratios are crucial for maximizing net returns in S&P 500 ETFs, as they directly impact long-term investment performance. Since ETFs passively track indices, their management costs are typically lower than actively managed funds. Comparing fees across major S&P 500 ETFs reveals notable differences. SPY, managed by State Street Global Advisors, has an expense ratio of 0.09%, while VOO and IVV, issued by Vanguard and iShares respectively, offer lower fees at 0.03%, making them more cost-effective for buy-and-hold investors. Additional costs such as bid-ask spreads and trading efficiency also impact ETF performance. Liquidity concerns arise when ETFs experience low trading volume, leading to wider spreads and potential price discrepancies.
Sector Allocations and Diversification Benefits
Sector allocations within S&P 500 ETFs play a crucial role in shaping investment strategies and portfolio diversification. The index is divided into multiple sectors, with technology, financials, and healthcare stocks often holding the largest weightings. Technology remains the dominant sector, accounting for approximately 27.6% of the S&P 500, followed by healthcare at 13.5% and financials at 10.4%. These weightings reflect the influence of industry leaders. Understanding sector weightings helps investors assess risk exposure and optimize portfolio diversification strategies. By diversifying across multiple sectors, investors can mitigate risks while capitalizing on growth opportunities within the S&P 500.
Risks and Limitations of S&P 500 ETFs
S&P 500 ETFs face market concentration risks due to their reliance on a few dominant companies. This heavy weighting toward mega-cap stocks, particularly in the technology sector, means that the performance of the index is increasingly dependent on a handful of companies. High-sensitivity to economic downturns and macroeconomic conditions is another limitation of S&P 500 ETFs. Additionally, the correlation between stock and bond markets has changed, reducing the diversification benefits of traditional portfolio strategies that rely on S&P 500 ETFs.
Balancing risk and reward in index funds requires strategic diversification. Additionally, diversifying into small-cap ETFs or international markets can reduce reliance on U.S. mega-cap stocks. By carefully managing risk, investors can ensure that their index fund investments align with their long-term financial goals.
How to Choose the Best Large-Cap S&P 500 ETF
Choosing the best large-cap S&P 500 ETF requires evaluating individual financial goals and investment time horizon. Investors seeking long-term growth may prioritize ETFs with lower expense ratios and strong historical performance, while those focused on liquidity and short-term trading might prefer funds with higher trading volume.
Comparing fund structures, liquidity, and expense efficiency is essential for selecting the right ETF. SPY, VOO, and IVV all track the S&P 500 but differ in their management strategies and cost structures. SPY, the oldest and most liquid S&P 500 ETF, has an expense ratio of 0.09%, making it a preferred choice for traders. VOO and IVV, with lower expense ratios of 0.03%, are more cost-effective for long-term investors. Liquidity considerations also play a key role. Understanding index tracking differences and trading accessibility further refines ETF selection.
Conclusion
Large-cap S&P 500 ETFs provide investors with an efficient way to gain broad market exposure while benefiting from diversification and cost efficiency. Funds such as SPY, VOO, and IVV offer distinct advantages in terms of expense ratios, liquidity, and index tracking, allowing investors to select options that best align with their financial goals.
While these ETFs provide stability and long-term growth potential, market concentration and economic fluctuations remain key considerations for portfolio management. Careful evaluation of sector weightings, fund structures, and trading costs helps investors optimize their ETF selection. By choosing the right S&P 500 ETF, investors can enhance their portfolio’s resilience while capitalizing on the growth of industry-leading companies.



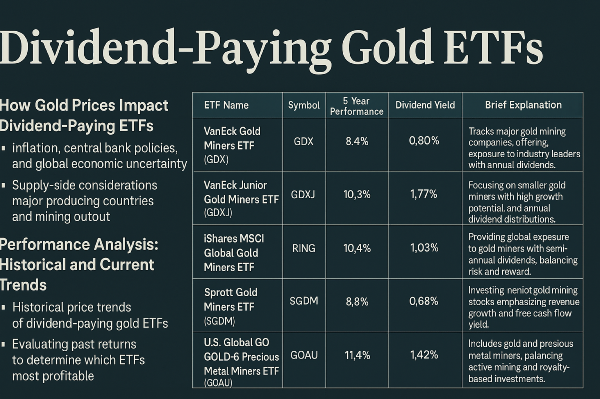



















Introduction
Large-cap S&P 500 ETFs provide investors with diversified exposure to the largest publicly traded companies in the United States. These funds track the S&P 500 index, ensuring broad market representation and stability in portfolio management. Selecting the best ETF requires evaluating key factors such as expense ratios, liquidity, sector allocations, and historical performance. Since the S&P 500 covers approximately 80% of the U.S. stock market by capitalization, investing in these ETFs allows individuals to participate in the growth of industry leaders while minimizing individual stock risk. Understanding these elements helps investors optimize their portfolios for long-term success.
Understanding Large-Cap S&P 500 ETFs
Large-cap S&P 500 ETFs are exchange-traded funds designed to track the performance of the S&P 500 index, which consists of the 500 largest publicly traded companies in the United States. These ETFs provide investors with broad market exposure, ensuring diversification across multiple sectors. Since they mirror the index’s composition, large-cap S&P 500 ETFs offer a straightforward way to invest in industry-leading companies without the need for individual stock selection.
Their passive management structure allows them to maintain low expense ratios, making them cost-effective investment options for long-term growth. These ETFs differ from other index funds and actively managed funds in multiple ways. Investing in large-cap S&P 500 ETFs offers several advantages, particularly for long-term investors. These funds provide stability by including well-established companies with strong financial positions, reducing overall portfolio risk.
Top Large-Cap S&P 500 ETFs in the Market
Large-cap S&P 500 ETFs such as SPY, VOO, and IVV are among the most widely traded funds, offering investors exposure to the largest companies in the U.S. stock market. SPY, managed by State Street Global Advisors, is the oldest and most liquid S&P 500 ETF, making it a preferred choice for traders. VOO, issued by Vanguard, and IVV, managed by iShares, provide similar exposure but with lower expense ratios, making them attractive for long-term investors. These ETFs track the S&P 500 index, ensuring broad diversification across multiple sectors while maintaining a focus on industry leaders.
Comparing the holdings and expense ratios of these ETFs reveals key differences. Despite tracking the same index, slight variations in fund structure and trading spreads can impact returns. The top holdings in these ETFs include mega-cap stocks such as Apple, Microsoft, and Amazon, which collectively account for a significant portion of the fund’s weightings. Sector distribution within SPY, VOO, and IVV highlights the dominance of technology, healthcare, and financial stocks. The concentration of mega-cap stocks within these ETFs can lead to higher volatility, particularly when leading companies experience price swings.
Performance Analysis of Large-Cap S&P 500 ETFs
Large-cap S&P 500 ETFs have historically delivered strong returns, closely mirroring the performance of the broader market. Funds such as SPY, VOO, and IVV have demonstrated consistent growth over the years, benefiting from the stability of large-cap stocks. However, these ETFs also experience volatility during market downturns, as they are directly influenced by macroeconomic conditions.
Investors should consider historical return trends alongside risk tolerance when selecting an S&P 500 ETF. Economic cycles play a crucial role in shaping the performance of large-cap S&P 500 ETFs. The long-term sustainability of index tracking remains a key advantage of large-cap S&P 500 ETFs. While short-term volatility may impact returns, the long-term trajectory of these ETFs remains positive, making them reliable options for wealth accumulation.
Expense Ratios and Cost Considerations
Low expense ratios are crucial for maximizing net returns in S&P 500 ETFs, as they directly impact long-term investment performance. Since ETFs passively track indices, their management costs are typically lower than actively managed funds. Comparing fees across major S&P 500 ETFs reveals notable differences. SPY, managed by State Street Global Advisors, has an expense ratio of 0.09%, while VOO and IVV, issued by Vanguard and iShares respectively, offer lower fees at 0.03%, making them more cost-effective for buy-and-hold investors. Additional costs such as bid-ask spreads and trading efficiency also impact ETF performance. Liquidity concerns arise when ETFs experience low trading volume, leading to wider spreads and potential price discrepancies.
Sector Allocations and Diversification Benefits
Sector allocations within S&P 500 ETFs play a crucial role in shaping investment strategies and portfolio diversification. The index is divided into multiple sectors, with technology, financials, and healthcare stocks often holding the largest weightings. Technology remains the dominant sector, accounting for approximately 27.6% of the S&P 500, followed by healthcare at 13.5% and financials at 10.4%. These weightings reflect the influence of industry leaders. Understanding sector weightings helps investors assess risk exposure and optimize portfolio diversification strategies. By diversifying across multiple sectors, investors can mitigate risks while capitalizing on growth opportunities within the S&P 500.
Risks and Limitations of S&P 500 ETFs
S&P 500 ETFs face market concentration risks due to their reliance on a few dominant companies. This heavy weighting toward mega-cap stocks, particularly in the technology sector, means that the performance of the index is increasingly dependent on a handful of companies. High-sensitivity to economic downturns and macroeconomic conditions is another limitation of S&P 500 ETFs. Additionally, the correlation between stock and bond markets has changed, reducing the diversification benefits of traditional portfolio strategies that rely on S&P 500 ETFs.
Balancing risk and reward in index funds requires strategic diversification. Additionally, diversifying into small-cap ETFs or international markets can reduce reliance on U.S. mega-cap stocks. By carefully managing risk, investors can ensure that their index fund investments align with their long-term financial goals.
How to Choose the Best Large-Cap S&P 500 ETF
Choosing the best large-cap S&P 500 ETF requires evaluating individual financial goals and investment time horizon. Investors seeking long-term growth may prioritize ETFs with lower expense ratios and strong historical performance, while those focused on liquidity and short-term trading might prefer funds with higher trading volume.
Comparing fund structures, liquidity, and expense efficiency is essential for selecting the right ETF. SPY, VOO, and IVV all track the S&P 500 but differ in their management strategies and cost structures. SPY, the oldest and most liquid S&P 500 ETF, has an expense ratio of 0.09%, making it a preferred choice for traders. VOO and IVV, with lower expense ratios of 0.03%, are more cost-effective for long-term investors. Liquidity considerations also play a key role. Understanding index tracking differences and trading accessibility further refines ETF selection.
Conclusion
Large-cap S&P 500 ETFs provide investors with an efficient way to gain broad market exposure while benefiting from diversification and cost efficiency. Funds such as SPY, VOO, and IVV offer distinct advantages in terms of expense ratios, liquidity, and index tracking, allowing investors to select options that best align with their financial goals.
While these ETFs provide stability and long-term growth potential, market concentration and economic fluctuations remain key considerations for portfolio management. Careful evaluation of sector weightings, fund structures, and trading costs helps investors optimize their ETF selection. By choosing the right S&P 500 ETF, investors can enhance their portfolio’s resilience while capitalizing on the growth of industry-leading companies.