Key Takeaways
To generate $3,000 a month in dividends, you'd typically need $900,000 to $1.2 million invested in dividend stocks yielding 3–4% annually. The required amount varies based on dividend yield—higher yields reduce the needed capital but may come with increased risk and lower growth potential.
Introduction
Dividend investing is a powerful strategy for generating passive income, allowing investors to build wealth over time without constantly buying and selling stocks. Many people set a goal of earning $3,000 per month in dividends because it provides a steady stream of income that can supplement retirement savings or even replace a traditional salary. To achieve this financial milestone, investors must consider several key factors, including the dividend yield of their portfolio, the total amount invested, and tax implications. Selecting the right mix of dividend-paying stocks, reinvesting earnings, and leveraging tax-advantaged accounts can accelerate progress toward this goal. By understanding these core principles, investors can craft a sustainable and effective plan for long-term financial independence.
Understanding Dividend Yield
Dividend yield is a key metric in dividend investing, representing the annual dividend income generated by a stock relative to its market price. It is expressed as a percentage and calculated by dividing the annual dividend per share by the stock’s current price. A higher yield means greater income per dollar invested, but investors must balance yield with sustainability, as excessively high yields can indicate financial instability. For example, if a stock priced at $100 pays an annual dividend of $4 per share, its yield is 4% ($4 ÷ $100 × 100). Comparing different yield levels—such as 2%, 4%, and 6%—can help investors estimate the capital required to achieve a targeted monthly dividend income. By understanding dividend yield, investors can make informed decisions about portfolio allocation and long-term income growth.
Calculating the Required Investment
Step 1: Determine Monthly Income Goal
To achieve a steady monthly income of $3,000 from dividends, investors must first set an annual income goal. Since $3,000 per month equates to $36,000 per year, the required investment depends on the dividend yield of the stocks or funds in the portfolio. Higher yields generate more income per dollar invested, but they may come with greater risks. Understanding this relationship helps investors determine the amount of capital needed to reach their desired passive income target.
Step 2: Estimate an Average Dividend Yield
Estimating an average dividend yield is crucial in calculating the necessary investment. For example, a portfolio with a low yield of 2%–3% would require approximately $1.2 million–$1.8 million to generate $36,000 annually. A moderate yield of 4%–6% lowers the required investment to $600,000–$900,000, while high-yield stocks offering 7%+ might only require around $514,000. However, higher yields often come with greater risks, such as dividend cuts or financial instability in the issuing company, so balancing yield and reliability is key.
Step 3: Factor in Taxes and Portfolio Growth
Investors must also account for taxes and portfolio growth when projecting their dividend income. Dividend earnings may be subject to taxation depending on the type of account in which they are held. Using tax-advantaged accounts like IRAs or reinvesting dividends through a dividend reinvestment plan (DRIP) can help offset tax burdens and increase overall portfolio value. Additionally, compound growth plays a significant role in long-term income generation, as reinvesting dividends leads to exponential accumulation over time.
External market factors, such as inflation and economic fluctuations, can affect the purchasing power of dividend income. Over time, inflation may erode the real value of payouts, making it necessary to adjust the investment strategy to maintain financial stability. Diversification across sectors and maintaining a balanced portfolio helps investors mitigate risks and sustain dividend income despite market volatility. By accounting for these variables, investors can create a strategic plan to reach their passive income goals efficiently.
Choosing the Right Dividend Stocks
Selecting the right dividend stocks is crucial for building a reliable income stream. Dividend aristocrats—companies with a long history of increasing payouts—offer stability and consistent growth, making them ideal for long-term investors. On the other hand, high-yield stocks provide larger immediate returns but often come with greater risks, such as dividend cuts or financial instability. Striking a balance between these categories can create a well-rounded portfolio that generates both steady and high returns.
Diversification plays a key role in reducing risk and maintaining consistent dividend income. Instead of relying on a single stock or sector, spreading investments across different industries ensures resilience against market fluctuations. Companies in sectors like consumer staples, utilities, healthcare, and real estate often maintain strong dividend payouts, even during economic downturns. Evaluating a company's financial health—looking at metrics such as payout ratios, earnings growth, and debt levels—helps determine sustainability and long-term income potential.
Strategies to Reach Your Investment Goal Faster
One of the fastest ways to reach your dividend investing goal is through dollar-cost averaging, a strategy that involves consistently investing a fixed amount over time. This approach reduces the impact of market volatility and allows investors to accumulate shares at various price points, maximizing long-term gains. Additionally, utilizing tax-advantaged accounts like IRAs or 401(k)s can help reduce tax burdens, allowing more of the earnings to compound over time.
Dividend reinvestment plans (DRIPs) further accelerate portfolio growth by automatically reinvesting dividend payments into additional shares. This strategy enhances compounding returns and increases income potential without requiring additional capital. By combining DRIPs with disciplined investing habits, investors can steadily build their portfolio and move closer to their passive income goals. Adopting these strategies ensures a more efficient and sustainable path toward financial independence through dividends.
Risks and Considerations
Dividend investing comes with inherent risks that investors must carefully manage to maintain a steady income stream. Market downturns can lead to declining stock prices and, in some cases, dividend cuts, reducing expected payouts. Companies facing financial strain or economic uncertainty may lower or suspend dividends to preserve cash. To mitigate these risks, investors should focus on companies with strong balance sheets and a history of consistent dividend payments, rather than chasing excessively high yields.
High-yield stocks can be tempting, but they often come with increased volatility and sustainability concerns. An abnormally high dividend yield may indicate financial distress, as falling stock prices inflate the yield percentage. To avoid these pitfalls, investors should assess payout ratios—companies paying out more than 80% of earnings may struggle to sustain dividends. A diversified portfolio that includes dividend aristocrats and well-established dividend-paying companies can provide long-term stability.
Conclusion
Monitoring and adjusting a dividend portfolio is essential for maximizing returns and reducing risk exposure. Economic conditions, sector shifts, and company performance can impact dividend income, making regular portfolio reviews necessary. Investors should consider reinvesting dividends, reallocating assets when needed, and staying informed about financial reports to ensure their strategy remains effective. Staying proactive helps protect against unforeseen changes and maintains consistent dividend growth.
Achieving financial independence through dividends requires patience, strategy, and disciplined investing. By understanding dividend yield, selecting reliable stocks, and employing tax-efficient investment strategies, investors can steadily build a portfolio capable of generating $3,000 per month in passive income. While risks exist, careful planning and diversification can mitigate uncertainties, turning dividend investing into a powerful wealth-building tool. With a long-term perspective and continuous portfolio optimization, financial independence through dividends is an attainable goal.
🚀 Your Ultimate Guide to Dividend Investing! 💰
Want to build reliable passive income? Looking to live off dividends? Start here with the top dividend insights:
🏆 Top Dividend Stock Picks
💰 Passive Income & Dividend Investing Strategies
🔍 How Much to Invest for BIG Dividend Income
⚡ Dividend Taxes & Smart Selling Strategies
🔗 Bookmark this guide & start building your dividend wealth today! 🚀💸



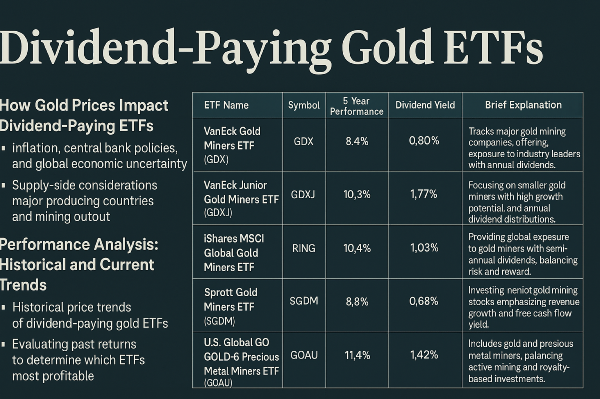
















Key Takeaways
To generate $3,000 a month in dividends, you'd typically need $900,000 to $1.2 million invested in dividend stocks yielding 3–4% annually. The required amount varies based on dividend yield—higher yields reduce the needed capital but may come with increased risk and lower growth potential.
Introduction
Dividend investing is a powerful strategy for generating passive income, allowing investors to build wealth over time without constantly buying and selling stocks. Many people set a goal of earning $3,000 per month in dividends because it provides a steady stream of income that can supplement retirement savings or even replace a traditional salary. To achieve this financial milestone, investors must consider several key factors, including the dividend yield of their portfolio, the total amount invested, and tax implications. Selecting the right mix of dividend-paying stocks, reinvesting earnings, and leveraging tax-advantaged accounts can accelerate progress toward this goal. By understanding these core principles, investors can craft a sustainable and effective plan for long-term financial independence.
Understanding Dividend Yield
Dividend yield is a key metric in dividend investing, representing the annual dividend income generated by a stock relative to its market price. It is expressed as a percentage and calculated by dividing the annual dividend per share by the stock’s current price. A higher yield means greater income per dollar invested, but investors must balance yield with sustainability, as excessively high yields can indicate financial instability. For example, if a stock priced at $100 pays an annual dividend of $4 per share, its yield is 4% ($4 ÷ $100 × 100). Comparing different yield levels—such as 2%, 4%, and 6%—can help investors estimate the capital required to achieve a targeted monthly dividend income. By understanding dividend yield, investors can make informed decisions about portfolio allocation and long-term income growth.
Calculating the Required Investment
Step 1: Determine Monthly Income Goal
To achieve a steady monthly income of $3,000 from dividends, investors must first set an annual income goal. Since $3,000 per month equates to $36,000 per year, the required investment depends on the dividend yield of the stocks or funds in the portfolio. Higher yields generate more income per dollar invested, but they may come with greater risks. Understanding this relationship helps investors determine the amount of capital needed to reach their desired passive income target.
Step 2: Estimate an Average Dividend Yield
Estimating an average dividend yield is crucial in calculating the necessary investment. For example, a portfolio with a low yield of 2%–3% would require approximately $1.2 million–$1.8 million to generate $36,000 annually. A moderate yield of 4%–6% lowers the required investment to $600,000–$900,000, while high-yield stocks offering 7%+ might only require around $514,000. However, higher yields often come with greater risks, such as dividend cuts or financial instability in the issuing company, so balancing yield and reliability is key.
Step 3: Factor in Taxes and Portfolio Growth
Investors must also account for taxes and portfolio growth when projecting their dividend income. Dividend earnings may be subject to taxation depending on the type of account in which they are held. Using tax-advantaged accounts like IRAs or reinvesting dividends through a dividend reinvestment plan (DRIP) can help offset tax burdens and increase overall portfolio value. Additionally, compound growth plays a significant role in long-term income generation, as reinvesting dividends leads to exponential accumulation over time.
External market factors, such as inflation and economic fluctuations, can affect the purchasing power of dividend income. Over time, inflation may erode the real value of payouts, making it necessary to adjust the investment strategy to maintain financial stability. Diversification across sectors and maintaining a balanced portfolio helps investors mitigate risks and sustain dividend income despite market volatility. By accounting for these variables, investors can create a strategic plan to reach their passive income goals efficiently.
Choosing the Right Dividend Stocks
Selecting the right dividend stocks is crucial for building a reliable income stream. Dividend aristocrats—companies with a long history of increasing payouts—offer stability and consistent growth, making them ideal for long-term investors. On the other hand, high-yield stocks provide larger immediate returns but often come with greater risks, such as dividend cuts or financial instability. Striking a balance between these categories can create a well-rounded portfolio that generates both steady and high returns.
Diversification plays a key role in reducing risk and maintaining consistent dividend income. Instead of relying on a single stock or sector, spreading investments across different industries ensures resilience against market fluctuations. Companies in sectors like consumer staples, utilities, healthcare, and real estate often maintain strong dividend payouts, even during economic downturns. Evaluating a company's financial health—looking at metrics such as payout ratios, earnings growth, and debt levels—helps determine sustainability and long-term income potential.
Strategies to Reach Your Investment Goal Faster
One of the fastest ways to reach your dividend investing goal is through dollar-cost averaging, a strategy that involves consistently investing a fixed amount over time. This approach reduces the impact of market volatility and allows investors to accumulate shares at various price points, maximizing long-term gains. Additionally, utilizing tax-advantaged accounts like IRAs or 401(k)s can help reduce tax burdens, allowing more of the earnings to compound over time.
Dividend reinvestment plans (DRIPs) further accelerate portfolio growth by automatically reinvesting dividend payments into additional shares. This strategy enhances compounding returns and increases income potential without requiring additional capital. By combining DRIPs with disciplined investing habits, investors can steadily build their portfolio and move closer to their passive income goals. Adopting these strategies ensures a more efficient and sustainable path toward financial independence through dividends.
Risks and Considerations
Dividend investing comes with inherent risks that investors must carefully manage to maintain a steady income stream. Market downturns can lead to declining stock prices and, in some cases, dividend cuts, reducing expected payouts. Companies facing financial strain or economic uncertainty may lower or suspend dividends to preserve cash. To mitigate these risks, investors should focus on companies with strong balance sheets and a history of consistent dividend payments, rather than chasing excessively high yields.
High-yield stocks can be tempting, but they often come with increased volatility and sustainability concerns. An abnormally high dividend yield may indicate financial distress, as falling stock prices inflate the yield percentage. To avoid these pitfalls, investors should assess payout ratios—companies paying out more than 80% of earnings may struggle to sustain dividends. A diversified portfolio that includes dividend aristocrats and well-established dividend-paying companies can provide long-term stability.
Conclusion
Monitoring and adjusting a dividend portfolio is essential for maximizing returns and reducing risk exposure. Economic conditions, sector shifts, and company performance can impact dividend income, making regular portfolio reviews necessary. Investors should consider reinvesting dividends, reallocating assets when needed, and staying informed about financial reports to ensure their strategy remains effective. Staying proactive helps protect against unforeseen changes and maintains consistent dividend growth.
Achieving financial independence through dividends requires patience, strategy, and disciplined investing. By understanding dividend yield, selecting reliable stocks, and employing tax-efficient investment strategies, investors can steadily build a portfolio capable of generating $3,000 per month in passive income. While risks exist, careful planning and diversification can mitigate uncertainties, turning dividend investing into a powerful wealth-building tool. With a long-term perspective and continuous portfolio optimization, financial independence through dividends is an attainable goal.
🚀 Your Ultimate Guide to Dividend Investing! 💰
Want to build reliable passive income? Looking to live off dividends? Start here with the top dividend insights:
🏆 Top Dividend Stock Picks
💰 Passive Income & Dividend Investing Strategies
🔍 How Much to Invest for BIG Dividend Income
⚡ Dividend Taxes & Smart Selling Strategies
🔗 Bookmark this guide & start building your dividend wealth today! 🚀💸