Introduction
Dividend ETFs are a popular choice among investors seeking steady income and long-term growth. These funds consist of a diversified portfolio of dividend-paying stocks, allowing investors to benefit from regular payouts while mitigating individual stock risks. One of the most critical aspects to consider when selecting a dividend ETF is its dividend yield, which represents the percentage of return an investor earns from dividends relative to the ETF’s share price. Understanding what constitutes a good dividend yield helps investors make informed decisions that align with their financial goals.
Understanding Dividend Yield
Dividend yield is calculated by dividing the annual dividends paid by the ETF by its current share price. This simple yet powerful metric allows investors to assess the income-generating potential of an ETF. However, a high yield does not always indicate a strong investment—while an elevated yield can be appealing, it may also signal underlying risks such as unsustainable payouts or declining stock prices. Conversely, a lower but consistent dividend yield might indicate a more stable investment with long-term growth potential. Investors must carefully weigh these factors before selecting a dividend ETF.
When evaluating dividend ETFs, several factors influence their yield, including interest rates, economic conditions, and the ETF’s underlying asset composition. For example, sectors like utilities and consumer staples often provide higher dividend yields due to their predictable cash flows, while technology-focused ETFs may have lower yields but higher capital appreciation potential. Additionally, a fund’s expense ratio can impact net dividend payouts, making it essential to consider total returns alongside yield. By analyzing these elements, investors can identify dividend ETFs that offer a balance between yield and long-term performance.
What Is Considered a "Good" Dividend Yield?
A "good" dividend yield for a dividend ETF depends on several factors, including industry benchmarks and sector comparisons. Generally, a dividend yield between 2% and 4% is considered solid for a well-diversified ETF, as it provides a steady income stream while maintaining sustainability. However, certain sectors, such as utilities and real estate, often exhibit higher yields, sometimes exceeding 5%, due to their stable cash flows. On the other hand, growth-focused sectors like technology may offer lower dividend yields but compensate with strong capital appreciation. Investors should analyze an ETF’s yield within its specific industry context to determine its attractiveness.
Yield sustainability is crucial when assessing dividend ETFs, as chasing high yields without considering long-term viability can be risky. Some ETFs may offer exceptionally high yields due to temporary market conditions or unsustainable payout practices, which can lead to dividend cuts in the future. A balanced approach involves examining dividend growth rates, payout ratios, and the financial health of the ETF’s underlying holdings. Companies with consistent earnings and a history of increasing dividends often indicate a stable and reliable yield, making them favorable choices for long-term investors.
Key Factors That Determine a Good Dividend Yield
Several key factors impact an ETF's dividend yield, including interest rates, economic conditions, and management fees. In periods of low interest rates, high-dividend ETFs may become more appealing as fixed-income alternatives, while rising rates could lead to decreased demand. Additionally, an ETF’s expense ratio can significantly affect net returns—higher fees reduce the actual dividend income received by investors. Evaluating an ETF’s dividend history alongside broader market trends ensures a well-informed investment strategy focused on both income and growth potential.
How to Analyze a Dividend ETF for Yield
When analyzing a dividend ETF for yield, investors should rely on key financial metrics to make informed decisions. One of the most important measures is the dividend yield, which calculates the percentage of return generated by dividends relative to the ETF’s share price. However, yield alone does not paint the full picture—other indicators such as the dividend payout ratio, earnings growth, and the fund’s historical performance provide deeper insight into its income stability. Reviewing an ETF’s holdings and assessing whether the underlying companies have a track record of consistent dividend payouts can also help determine its reliability.
Dividend growth over time is a crucial factor in selecting a strong dividend ETF. While some funds may offer high yields, they could suffer from declining payouts if their holdings experience financial distress. A preferable approach is to focus on ETFs with a history of increasing dividends, as this suggests a sustainable income stream that can withstand market fluctuations. Investors can use tools like financial news platforms, ETF research websites, and fund prospectuses to compare different ETFs and track dividend growth trends over time. Keeping an eye on dividend consistency, rather than just yield percentage, is essential for long-term portfolio success.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
One of the most common mistakes investors make is chasing high yields without considering underlying risks. Extremely high dividend yields may indicate financial instability, as they could be driven by stock price declines rather than strong earnings. Additionally, overlooking total return—combining both dividend payouts and share price appreciation—can lead to short-sighted investment choices. Tax implications also play a significant role, as dividends may be subject to different tax treatments depending on whether they are qualified or ordinary. By understanding these pitfalls, investors can build a balanced dividend ETF portfolio that maximizes income while minimizing risks.
Conclusion
Selecting a dividend ETF with a strong yield requires careful evaluation of various financial metrics, sector benchmarks, and long-term sustainability. Investors should prioritize funds that offer stable and growing dividend payouts rather than chasing excessively high yields, which can sometimes signal financial instability. Considering factors like expense ratios, dividend consistency, and overall total return will help in making well-informed investment decisions. A balanced approach—where yield is weighed alongside risk management and growth potential—ensures a portfolio that provides steady income while fostering long-term capital appreciation. By conducting thorough research and leveraging financial tools, investors can confidently choose dividend ETFs that align with their financial goals.
🚀 Master Dividend Investing – Unlock Passive Income 💰
Looking to supercharge your portfolio and live off dividends? Dive into these expert resources:
🏆 Top Dividend Stocks & Investing Strategies
💰 Dividend Funds & High-Yield ETFs
⚡ Dividend Essentials & Tax Strategies
🔗 Bookmark this guide & start your journey to financial independence! 🚀💸









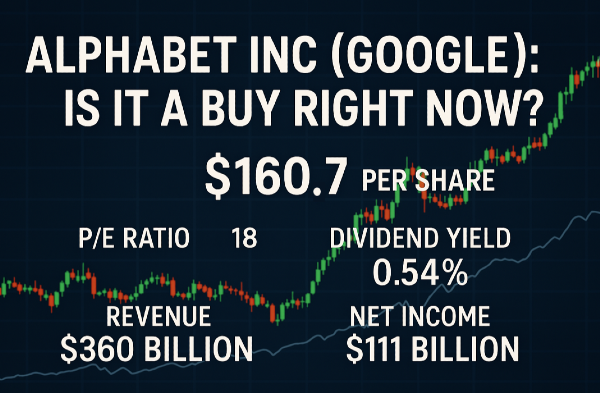




Introduction
Dividend ETFs are a popular choice among investors seeking steady income and long-term growth. These funds consist of a diversified portfolio of dividend-paying stocks, allowing investors to benefit from regular payouts while mitigating individual stock risks. One of the most critical aspects to consider when selecting a dividend ETF is its dividend yield, which represents the percentage of return an investor earns from dividends relative to the ETF’s share price. Understanding what constitutes a good dividend yield helps investors make informed decisions that align with their financial goals.
Understanding Dividend Yield
Dividend yield is calculated by dividing the annual dividends paid by the ETF by its current share price. This simple yet powerful metric allows investors to assess the income-generating potential of an ETF. However, a high yield does not always indicate a strong investment—while an elevated yield can be appealing, it may also signal underlying risks such as unsustainable payouts or declining stock prices. Conversely, a lower but consistent dividend yield might indicate a more stable investment with long-term growth potential. Investors must carefully weigh these factors before selecting a dividend ETF.
When evaluating dividend ETFs, several factors influence their yield, including interest rates, economic conditions, and the ETF’s underlying asset composition. For example, sectors like utilities and consumer staples often provide higher dividend yields due to their predictable cash flows, while technology-focused ETFs may have lower yields but higher capital appreciation potential. Additionally, a fund’s expense ratio can impact net dividend payouts, making it essential to consider total returns alongside yield. By analyzing these elements, investors can identify dividend ETFs that offer a balance between yield and long-term performance.
What Is Considered a "Good" Dividend Yield?
A "good" dividend yield for a dividend ETF depends on several factors, including industry benchmarks and sector comparisons. Generally, a dividend yield between 2% and 4% is considered solid for a well-diversified ETF, as it provides a steady income stream while maintaining sustainability. However, certain sectors, such as utilities and real estate, often exhibit higher yields, sometimes exceeding 5%, due to their stable cash flows. On the other hand, growth-focused sectors like technology may offer lower dividend yields but compensate with strong capital appreciation. Investors should analyze an ETF’s yield within its specific industry context to determine its attractiveness.
Yield sustainability is crucial when assessing dividend ETFs, as chasing high yields without considering long-term viability can be risky. Some ETFs may offer exceptionally high yields due to temporary market conditions or unsustainable payout practices, which can lead to dividend cuts in the future. A balanced approach involves examining dividend growth rates, payout ratios, and the financial health of the ETF’s underlying holdings. Companies with consistent earnings and a history of increasing dividends often indicate a stable and reliable yield, making them favorable choices for long-term investors.
Key Factors That Determine a Good Dividend Yield
Several key factors impact an ETF's dividend yield, including interest rates, economic conditions, and management fees. In periods of low interest rates, high-dividend ETFs may become more appealing as fixed-income alternatives, while rising rates could lead to decreased demand. Additionally, an ETF’s expense ratio can significantly affect net returns—higher fees reduce the actual dividend income received by investors. Evaluating an ETF’s dividend history alongside broader market trends ensures a well-informed investment strategy focused on both income and growth potential.
How to Analyze a Dividend ETF for Yield
When analyzing a dividend ETF for yield, investors should rely on key financial metrics to make informed decisions. One of the most important measures is the dividend yield, which calculates the percentage of return generated by dividends relative to the ETF’s share price. However, yield alone does not paint the full picture—other indicators such as the dividend payout ratio, earnings growth, and the fund’s historical performance provide deeper insight into its income stability. Reviewing an ETF’s holdings and assessing whether the underlying companies have a track record of consistent dividend payouts can also help determine its reliability.
Dividend growth over time is a crucial factor in selecting a strong dividend ETF. While some funds may offer high yields, they could suffer from declining payouts if their holdings experience financial distress. A preferable approach is to focus on ETFs with a history of increasing dividends, as this suggests a sustainable income stream that can withstand market fluctuations. Investors can use tools like financial news platforms, ETF research websites, and fund prospectuses to compare different ETFs and track dividend growth trends over time. Keeping an eye on dividend consistency, rather than just yield percentage, is essential for long-term portfolio success.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
One of the most common mistakes investors make is chasing high yields without considering underlying risks. Extremely high dividend yields may indicate financial instability, as they could be driven by stock price declines rather than strong earnings. Additionally, overlooking total return—combining both dividend payouts and share price appreciation—can lead to short-sighted investment choices. Tax implications also play a significant role, as dividends may be subject to different tax treatments depending on whether they are qualified or ordinary. By understanding these pitfalls, investors can build a balanced dividend ETF portfolio that maximizes income while minimizing risks.
Conclusion
Selecting a dividend ETF with a strong yield requires careful evaluation of various financial metrics, sector benchmarks, and long-term sustainability. Investors should prioritize funds that offer stable and growing dividend payouts rather than chasing excessively high yields, which can sometimes signal financial instability. Considering factors like expense ratios, dividend consistency, and overall total return will help in making well-informed investment decisions. A balanced approach—where yield is weighed alongside risk management and growth potential—ensures a portfolio that provides steady income while fostering long-term capital appreciation. By conducting thorough research and leveraging financial tools, investors can confidently choose dividend ETFs that align with their financial goals.
🚀 Master Dividend Investing – Unlock Passive Income 💰
Looking to supercharge your portfolio and live off dividends? Dive into these expert resources:
🏆 Top Dividend Stocks & Investing Strategies
💰 Dividend Funds & High-Yield ETFs
⚡ Dividend Essentials & Tax Strategies
🔗 Bookmark this guide & start your journey to financial independence! 🚀💸